Since generative artificial intelligence (generative AI, or GenAI) began gaining traction in the early 2020s, it’s gone from a media buzzword to a practical business tool. Whether used to refine marketing campaigns or suggest improvements to a product’s design, AI has proven useful in countless industries. With nearly 80% of businesses using AI in some capacity in 2024, the real question is no longer whether a company will use AI, but how it will do so.
At Qualtrics, we’ve been paying close attention to how this shift is unfolding, and as the technology continues to evolve, so does the way companies use it to stay ahead. With that in mind, today we’re looking at the many ways businesses are using AI in 2025.
Why businesses are turning to AI
AI is quickly becoming a standard tool in the business toolkit. According to AI statistics, in 2025, three out of four companies now regularly use AI for at least one function, a sharp increase from just two years ago. For example, nearly every Fortune 500 company (99% to be exact) has integrated AI into its hiring process, from screening applicants to predicting success in a role. At the employee level, AI is also used for professional development, with 83% of professionals using AI tools to learn new workplace skills.
Financially, the impact is even more tangible. Every dollar invested in generative AI now yields an average return of $3.70, with leading companies reporting returns up to 10 times that figure. With the AI market projected to surpass $1.3 trillion by 2032 and 92% of organizations planning to increase their investment over the next three years, it’s clear that people are putting their faith in AI to boost profits. As such, it’s fair to say AI is here to stay, and businesses that embrace it are seeing stronger performance and a clearer competitive edge.
Is AI profitable?
AI has proven useful in a variety of ways across different industries. In strategy and corporate finance, 70% of companies report increased revenue thanks to GenAI tools that analyze data faster and identify more innovative opportunities. On the mercantile side, supply chain teams are using AI to streamline inventory and logistics, and half of them already report cost reductions. Marketing and sales departments are also heavy users, with 42% of all businesses adopting GenAI for content creation, customer engagement, and automation. Even customer service has seen an explosive growth in AI adoption, increasing by over 2000% since January of 2025.
The creative side of AI is growing too. While AI may be able to replace certain tedious tasks, it is also becoming a sort of digital sounding board, used as an extension of how people think, work, and collaborate. About 63% of companies use GenAI to write text content, 36% to generate images, and 27% to assist with coding. Millennials, as the largest portion of the workforce, are leading the charge, with 90% feeling comfortable using AI at work and 81% eager to participate in designing AI tools themselves.
Global momentum and market leadership
AI business statistics show that artificial intelligence adoption is spreading rapidly across the world. There are now more than 70,000 AI companies globally, and the most successful startups are seeing an average of $3.48 million in revenue per employee, six times that of traditional SaaS firms. The United States reigns at the top, and in 2024 alone, U.S. private AI investment reached $109.1 billion. This level of investment is fueling innovation at a scale unmatched by any other nation, outpacing China and the United Kingdom’s spending by twelve and four times, respectively.
Nearly 90% of the world’s most notable AI models are the product of private industry rather than academia, demonstrating just how important businesses are in shaping AI innovation.
While large businesses like Nvidia, which recently became the first to exceed $5 trillion in market value, have become critical players, small businesses in the U.S. are also a part of the pie. About 89% now use AI in their daily operations, from managing finances to enhancing customer service. An additional 60% of small business owners who use AI say it has improved employee productivity and job satisfaction. While executives and senior managers remain the most active users, adoption among entry-level employees and interns is rising steadily as AI tools become more intuitive and accessible to regular users.
Viewed as a whole, these 2025 AI statistics reveal that this tech is becoming a part of the everyday rhythm of business. Rather than replacing the human touch, it’s being used to shape strategy, innovate, and deepen the connection between companies and their customers. The companies seeing the greatest success are those that use AI not just to automate, but to amplify existing human skills and talents.
If your organization is ready to put data to work with the latest in AI analytics technology, we can help. At Qualtrics, we empower businesses to use AI to understand, predict, and act with confidence. Contact us today to learn how your company can transform insights into intelligent action and improve brand experience.
25 Statistics on business use of AI in 2025
| Stat | Additional Info |
| Global | |
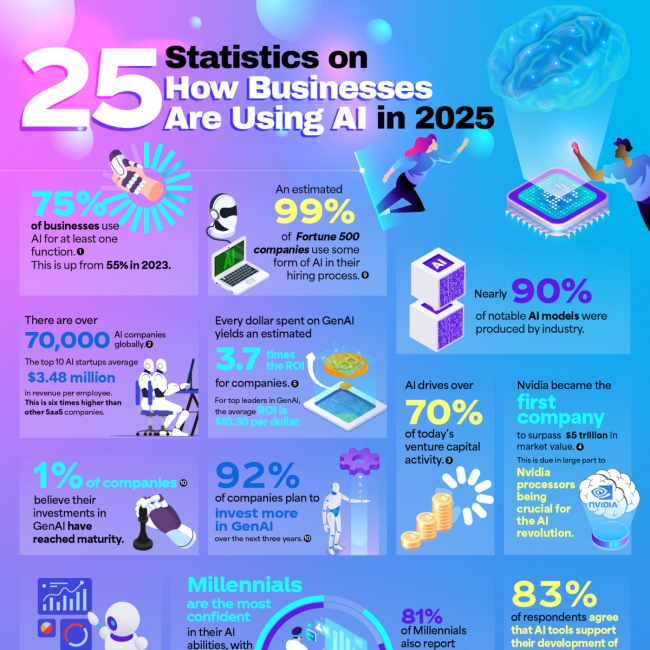
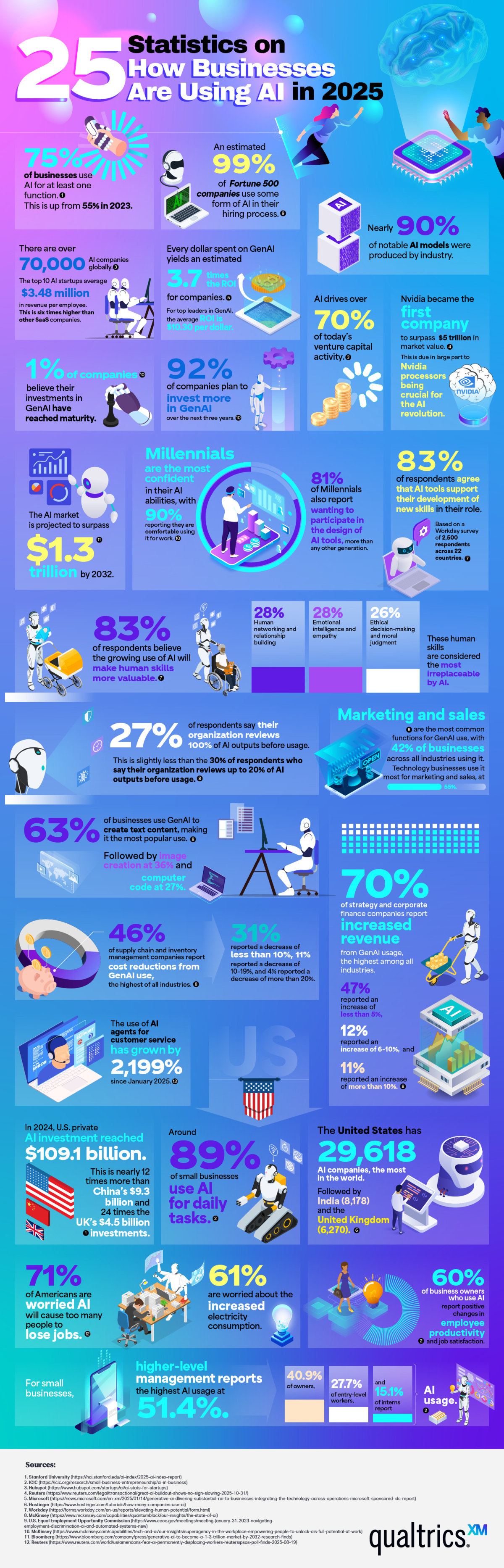
| 75% of businesses use AI for at least one function.1 | This is up from 55% in 2023. |
| An estimated 99% of Fortune 500 companies use some form of AI in their hiring process.9 | |
| Nearly 90% of notable AI models were produced by industry.1 | |
| There are over 70,000 AI companies globally.3 | The top 10 AI startups average $3.48 million in revenue per employee. This is six times higher than other SaaS companies. |
| AI drives over 70% of today’s venture capital activity.3 | |
| Nvidia became the first company to surpass $5 trillion in market value.4 | This is due in large part to Nvidia processors being crucial for the AI revolution. |
| Every dollar spent on GenAI yields an estimated 3.7 times the ROI for companies.5 | For top leaders in GenAI, the average ROI is $10.30 per dollar. |
| 1% of companies believe their investments in GenAI have reached maturity.10 | |
| 92% of companies plan to invest more in GenAI over the next three years.10 | |
| The AI market is projected to surpass $1.3 trillion by 2032.11 | |
| Millennials are the most confident in their AI abilities, with 90% reporting they are comfortable using it for work.10 | 81% of Millennials also report wanting to participate in the design of AI tools, more than any other generation. |
| 83% of respondents agree that AI tools support their development of new skills in their role.7 | Based on a Workday survey of 2,500 respondents across 22 countries. |
| 83% of respondents believe the growing use of AI will make human skills more valuable.7 | Human networking and relationship building (28%), emotional intelligence and empathy (28%), and ethical decision-making and moral judgment (26%) are considered the most irreplaceable by AI. |
| 27% of respondents say their organization reviews 100% of AI outputs before usage.8 | This is slightly less than the 30% of respondents who say their organization reviews up to 20% of AI outputs before usage. |
| Marketing and sales are the most common functions for GenAI use, with 42% of businesses across all industries using it.8 | Technology businesses use it most for marketing and sales, at 55%. |
| 63% of businesses use GenAI to create text content, making it the most popular use.8 | Followed by image creation at 36% and computer code at 27%. |
| 70% of strategy and corporate finance companies report increased revenue from GenAI usage, the highest among all industries.8 | 47% reported an increase of less than 5%, 12% reported an increase of 6–10%, and 11% reported an increase of more than 10%. |
| 46% of supply chain and inventory management companies report cost reductions from GenAI use, the highest of all industries.8 | 31% reported a decrease of less than 10%, 11% reported a decrease of 10–19%, and 4% reported a decrease of more than 20%. |
| The use of AI agents for customer service has grown by 2,199% since January 2025.13 | |
| United States | |
| In 2024, U.S. private AI investment reached $109.1 billion.1 | This is nearly 12 times more than China’s $9.3 billion and 24 times the UK’s $4.5 billion investments. |
| The United States has 29,618 AI companies, the most in the world.6 | Followed by India (8,178) and the United Kingdom (6,270). |
| Around 89% of small businesses use AI for daily tasks.2 | |
| 71% of Americans are worried AI will cause too many people to lose jobs.12 | 61% are worried about the increased electricity consumption. |
| 60% of business owners who use AI report positive changes in employee productivity and job satisfaction.2 | |
| For small businesses, higher-level management reports the highest AI usage at 51.4%.2 | 40.9% of owners, 27.7% of entry-level workers, and 15.1% of interns report AI usage. |
Sources
2 ICIC
3 Hubspot
4 Reuters
7 Workday
8 McKinsey
9 U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission
10 McKinsey
11 Bloomberg
12 Reuters