Author: Ray Gerber
Is it time to rethink traditional journey mapping methods?
In an era marked by rapid changes in consumer behaviour and heightened expectations, traditional methods of customer journey mapping are, rightly, coming under scrutiny.
But what does that mean for the people looking to maximize each journey? Put simply: it’s time to adapt.
Traditionally, journey maps have been static – often created through time-consuming processes that involve extensive research and data collection. These methods, while thorough, tend to be resource-intensive and costly. More importantly, they lack the agility to adapt to fast-paced changes in customer behaviour and preferences.
In a digital age where customer interactions and expectations evolve at an unprecedented rate, relying on these static maps can leave businesses trailing behind, operating on outdated assumptions and missing crucial opportunities for engagement and improvement.
All of this presents us with a pressing need: shifting towards more dynamic, data-driven journey mapping techniques. But it’s a shift that goes much further than simply keeping pace with change; it’s about embracing a more responsive, customer-centric approach that aligns closely with the ever-evolving journey of today’s consumers.
And that’s exactly what we’ll be covering in this article – starting with some of the basics…
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual interpretation of the overall relationship a customer has with an organisation, service, product, or brand – over time and across different channels. It helps businesses step into their customers’ shoes and see their business from the customer’s perspective.
Crucially, a customer journey map also allows companies to gain insights into common customer pain points, how they interact with the brand, and the pathways they take from the first engagement to a long-term relationship.
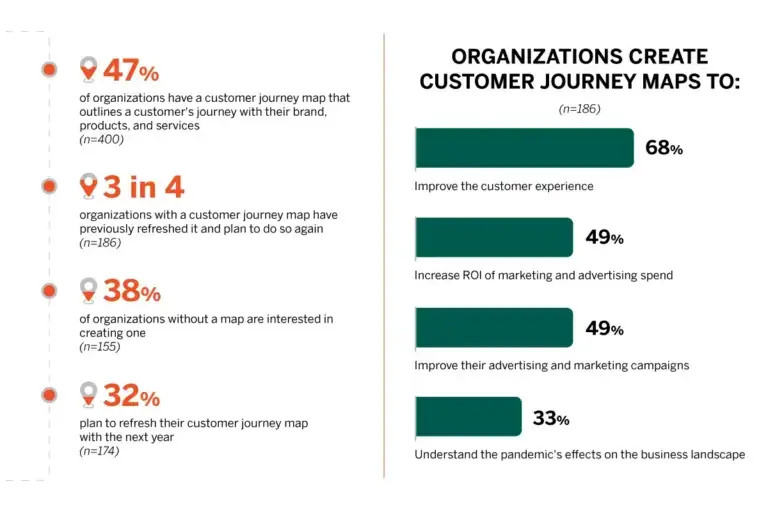
Image from: The Power of Customer Journey Mapping 2023 Hanover Research
How Businesses View Customer Journey maps
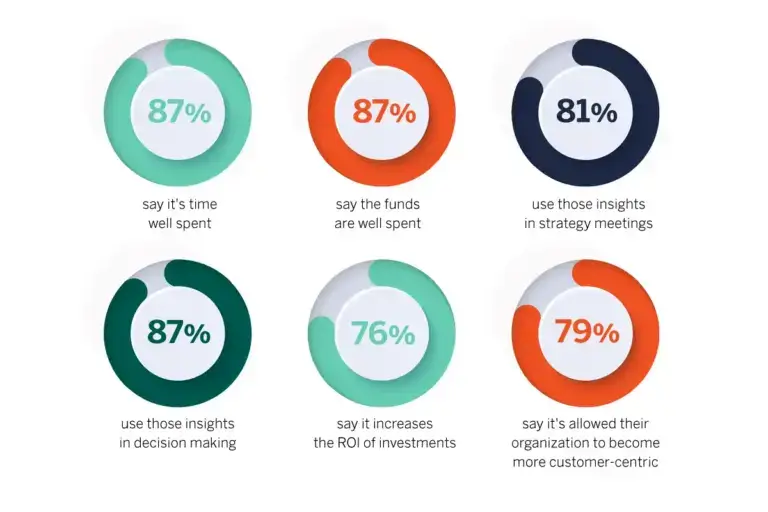
Image from: The Power of Customer Journey Mapping 2023 Hanover Research
Why is a customer journey map important?
An accurate, adaptable customer journey map is a means to enable positive change. In an era where customer experience is a key differentiator, journey maps serve as crucial tools.
They help businesses:
- Understand and empathise with customers.
- Identify and address pain points and bottlenecks in the customer experience.
- Align internal teams around a shared understanding of customer needs and experiences.
- Optimize and personalize customer interactions at each touchpoint.
- Strategically plan enhancements to products, services, and processes.
But there’s a problem: not every company that creates customer journey maps knows how to put them to work. In 2019, Gartner reported that while some 82% of organizations have created customer journey maps, only 47% are using them effectively.
Worse still, in 2022, the Technology Services Industry Association found that only 29% of customer success teams who created a customer journey map actually used it at all.
Free eBook: The ultimate guide to customer journey mapping
Components of a customer journey map
Ok, so what actually goes into a successful, usable customer journey map?
A well-constructed map comprises a myriad component plays a distinct role in painting a complete picture of the customer’s journey, with valuable insights that can drive strategic improvements and foster deeper customer connections.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Audience | Defined by customer personas representing different segments of your target market, based on data and insights about customers’ demographics, behaviors, motivations, and goals. |
| Start and Completion/Abort Conditions | Clearly defined starting points (e.g., first contact with a brand) and end conditions (e.g., purchase, repeat purchase, or churn) that mark the journey’s scope. |
| Lifecycle Stages | The phases a customer goes through in their journey with a brand, typically including awareness, consideration, decision, retention, and advocacy. |
| Touchpoints and Channels | Various points of interaction between the customer and the brand, and the channels (digital and physical) where these interactions occur. |
| Emotions and Motivations | Insights into how customers feel at different stages and what drives their decisions. |
| Pain Points and Opportunities | Challenges customers face during their journey and opportunities for the business to improve the experience. |
| Metrics and Data Points | Key performance indicators and metrics that help measure the success of the customer journey at various stages. |
Here is an example of what a full customer journey map looks like with all this information collated:
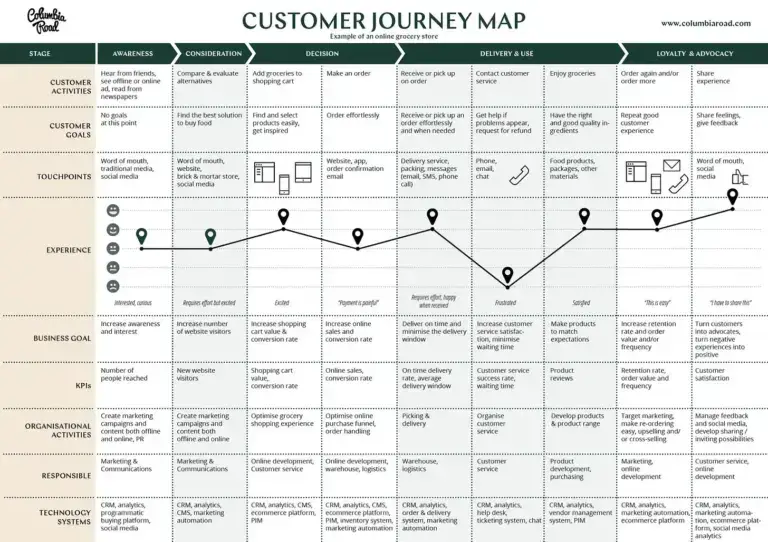
Image from: www.Columbiaroad.com
This customer journey map is a visual representation of the stages a customer goes through when interacting with an online grocery store, structured into six stages: Awareness, Consideration, Decision, Delivery & Use, and Loyalty & Advocacy.
Awareness:
The customer learns about the store through word-of-mouth, media, or online. The goal is to increase awareness and interest, supported by marketing campaigns and social media.
Consideration:
The customer compares options and looks for the best solutions. The business aims to increase the number of website visitors through marketing and communications.
Decision:
Adding items to the cart and making a purchase. The experience should be effortless, with the business goal of increasing sales and conversion rates, supported by an optimised online purchasing funnel.
Delivery & Use:
The customer receives their order. The goal is to deliver on time and ensure satisfaction, achieved by efficient logistics and customer service.
Loyalty & Advocacy:
Post-purchase, customers may reorder or share their experience. The business aims to increase retention and turn customers into advocates, managed by customer service and marketing.
Each stage lists customer activities, goals, touchpoints, experiences, business goals, KPIs (Key Performance Indicators), organisational activities, and technology systems used. The map charts the emotional journey with peaks (excitement) and valleys (effort or frustration), aiming to provide insights into how to enhance the customer experience at each stage.
Limitations of the traditional approach to journey mapping
While traditional journey mapping has been a cornerstone for understanding and visualising the customer’s path through various touchpoints with a brand, a static, one-time snapshot approach has its limitations.
Here are seven reasons why conventional mapping methods may no longer suffice in today’s dynamic market environment:
Static nature
Traditional journey maps are often static, representing a fixed snapshot of the customer journey. This rigidity fails to account for the fluid and ever-changing nature of customer interactions and preferences, leading to a map that quickly becomes outdated as market dynamics shift.
Time-consuming and resource-intensive
The creation of traditional journey maps typically involves extensive research, including customer interviews, surveys, and workshops. This process is not only time-consuming but also demands significant resources, both in terms of manpower and financial investment.
Lack of personalisation
Traditional maps tend to generalise the customer experience, based on averaged data and broad customer personas. This approach overlooks the nuances and individual variations in customer behaviour, resulting in a one-size-fits-all model that may not accurately reflect the experiences of different customer segments.
Limited real-time insights
The traditional journey mapping process does not incorporate real-time data. Consequently, businesses miss out on the opportunity to respond promptly to immediate changes in customer behaviour or feedback, potentially leading to missed opportunities for engagement and improvement.
Over-reliance on assumptions
Often, these maps are created based on assumptions about customer behaviour and preferences, rather than hard data. This can lead to a disconnect between what businesses perceive to be the customer journey and the actual experiences of their customers.
Inadequate measurement of impact
Traditional journey maps do not always include clear metrics or KPIs to measure the impact of various touchpoints on customer behaviour. This lack of quantifiable measurement makes it challenging to assess the effectiveness of different aspects of the journey and to make data-driven improvements.
Difficulty in aligning cross-functional teams
Given their static nature, traditional maps can struggle to align different teams around a unified, evolving customer strategy. Different departments may interpret the journey map differently, leading to inconsistent customer experiences.
Meeting modern business challenges
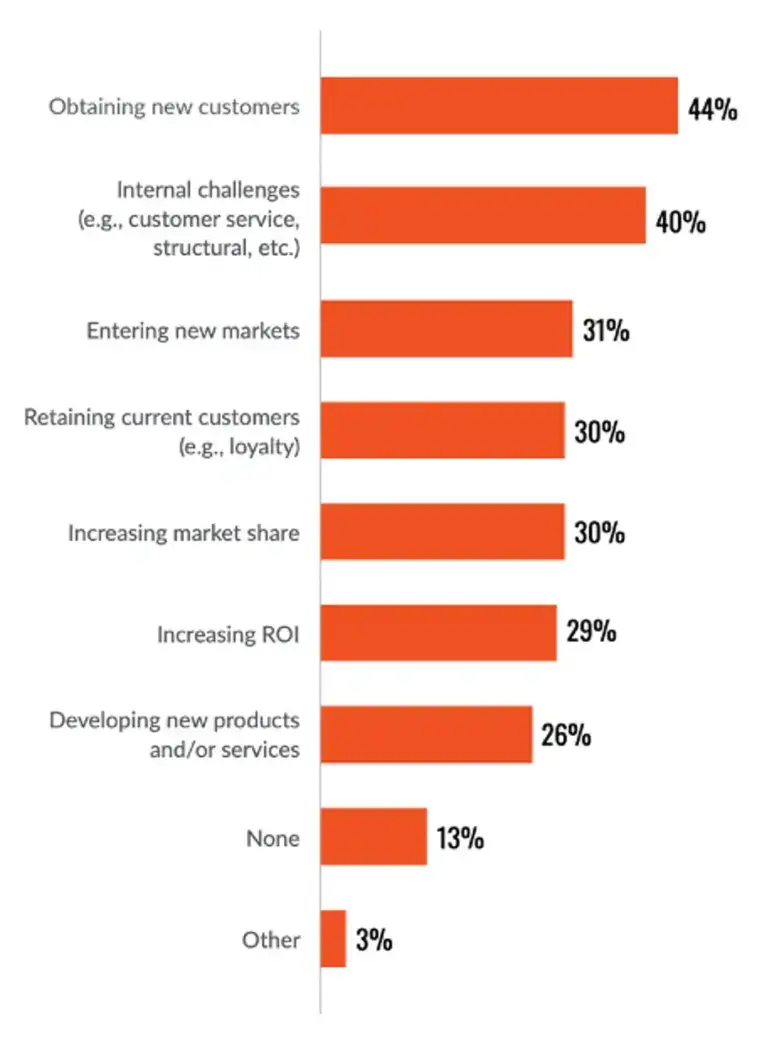
© 2023 Hanover Research CORWP0123
The image above lists several initiatives that have become more challenging for businesses: obtaining new customers, internal challenges, entering new markets, retaining current customers, increasing market share, increasing ROI, and developing new products/services.
These are universal challenges, and they all play a role in how journey mapping needs to evolve…
Obtaining new customers & entering new markets
Traditional journey maps may not account for the changing behaviours of different market segments – or the nuances of new market contexts. Dynamic journey maps that integrate behavioural data can provide a more accurate and adaptable model for understanding the customer journey in different markets.
Internal challenges
Static journey maps might not reflect the internal process changes quickly enough. A dynamic, behaviour-based map offers real-time insights into operational issues that affect customer experience.
Retaining current customers
Traditional journey maps often lack the granularity to understand the shifting loyalty drivers. Dynamic mapping can highlight evolving customer needs and preferences, helping to tailor experiences that enhance loyalty.
Increasing market share & ROI
By focusing on actual behaviours rather than assumptions, dynamic journey maps can uncover opportunities for differentiation and value creation, directly influencing market share and return on investment.
Developing new products and services
Traditional maps might miss rapid changes in customer expectations and emerging trends. Behavioural-based mapping processes can identify new needs and opportunities for innovation, leading to more timely and relevant product development.
Evolving your customer journey maps
The challenges listed above all indicate a need for more sophisticated journey mapping that can adapt to the complex nature of customer behaviors and business environments.
So, with that in mind, let’s look at two ways that your journey maps can evolve…
1. Adding Voice of the Customer insights to journey maps
The integration of Voice of the Customer (VoC) data into journey maps marks the first significant evolution in the approach to understanding customer experiences.
VoC data transforms journey maps from static, assumption-based models into dynamic tools that reflect real customer feedback and sentiments. VoC data includes direct input from customers, such as survey responses, customer reviews, feedback forms, and social media comments. By integrating this data, journey maps become more aligned with the customer’s actual experiences and perceptions, providing a richer, more nuanced view of their journey.
Methodology for incorporating VoC data:
- Data collection: The first step involves gathering VoC data through various channels. This includes structured methods like surveys and feedback forms, as well as unstructured data from social media, customer reviews, and call centre transcripts.
- Data analysis: The collected data is then analysed to extract meaningful insights. This involves identifying common themes, sentiments, pain points, and moments of delight in the customer journey.
- Mapping VoC to journey stages: The insights are mapped to corresponding stages in the customer journey. This process helps in visualising how customer sentiments and experiences vary across different touchpoints.
- Iterative refinement: The journey map is continuously updated with new VoC data, ensuring it remains relevant and reflective of the current customer experience.
The value of VoC-enhanced customer journey maps:
Customer-centricity
VoC-enhanced maps put the customer’s voice at the forefront, ensuring that strategies and improvements are directly aligned with customer needs and expectations.
Improved accuracy
These maps are more accurate in depicting the customer journey, as they are based on actual customer feedback rather than assumptions.
Enhanced engagement insights
VoC data provides deeper insights into why customers behave in certain ways, enabling businesses to understand the motivations behind customer actions.
Strategic decision making
Armed with precise customer feedback, businesses can make more informed decisions about product improvements, marketing strategies, and customer service enhancements.
Identifying pain points and opportunities
VoC data highlights specific areas where customers face challenges or where there are opportunities to enhance the experience, guiding targeted improvements.
Are there downsides of VoC-powered customer journey maps?
Integrating VoC data helps make these maps more reflective of the actual customer experience, but doing so is not without its limitations:
Subjectivity and bias
VoC data is inherently subjective, reflecting the perceptions and opinions of customers. This can introduce bias, as the feedback may not always represent the broader customer base or accurately reflect actual behaviours.
Lag in feedback
VoC data often captures customer sentiments after an experience has occurred. This delay can result in missed opportunities to address issues in real-time, reducing the ability to proactively enhance the customer experience.
Incomplete picture
Relying solely on VoC data can lead to gaps in understanding the customer journey. Customers may not accurately recall all their interactions or may only provide feedback on certain aspects of their experience, leaving out key touchpoints.
Challenges in quantification
Translating qualitative VoC data into actionable insights can be challenging. Quantifying sentiments and opinions for strategic decision-making requires sophisticated analysis, which can be resource-intensive.
Limited predictive power
While VoC data offers insights into past and present customer experiences, it has limited capability in predicting future behaviors or trends. This restricts the ability of businesses to anticipate customer needs proactively.
Understanding these limitations is important if we’re going to understand what’s still lacking from our customer journey maps – even with the added benefit of VoC data.
So what’s the solution here? Put simply: smarter insights on human behaviour.
2. Adding behavioural insights to journey maps
The integration of actual customer behavioural data alongside Voice of the Customer (VoC) insights represents the second evolution in journey mapping.
That’s because this approach not only considers what customers say, but also what they actually do – providing a more holistic view of the customer experience. The result is a comprehensive view of the customer journey that encompasses both the tangible actions customers take and their perceptions and reactions to those experiences.
A key advantage of this integrated approach is its capacity for real-time responsiveness. Behavioural data, by its nature, offers insights as they happen, enabling businesses to swiftly adapt to emerging trends, shifts in customer behaviour, and changing preferences. This agility is crucial in today’s fast-paced market, where customer expectations and behaviours can evolve rapidly.
Moreover, the inclusion of behavioural data opens the door to predictive analytics. By analysing patterns and trends in customer behaviour, businesses can move beyond reactive strategies to a more proactive stance. Predictive modelling, powered by this rich data integration, allows for the anticipation of future customer needs and trends. This forward-looking perspective is invaluable for businesses aiming to stay ahead of customer expectations and continuously refine their customer experience strategies.
How to collect behavioural data
Integrating behavioural and VoC Insights into journey maps begins with a comprehensive data collection phase, where behavioural data—encompassing website interactions, purchase history, and customer service engagements—is gathered alongside Voice of the Customer (VoC) feedback. This rich tapestry of information is typically sourced from digital analytics tools, CRM systems, and customer feedback platforms, providing a multifaceted view of customer interactions.
The subsequent phase involves a meticulous process of data analysis and synthesis. Here, advanced analytics and AI tools play a crucial role, sifting through large datasets to uncover patterns and correlations that might not be immediately apparent. This deep dive into the data helps in extracting meaningful insights that are crucial for the next step.
Once the data is analyzed, the integration process begins. The insights gleaned from both behavioural and VoC data are carefully mapped onto the customer journey.
This crucial step involves pinpointing how customer actions, as indicated by the behavioural data, and their feedback, as captured through VoC, align and interact at each stage of the journey. This mapping creates a more nuanced and comprehensive view of the customer experience, highlighting areas of alignment and divergence between what customers do and what they say.
Crucially, unlike traditional static journey maps, these dynamic maps are not set in stone. They are regularly updated with new data, ensuring they continuously evolve and remain reflective of the current customer experience. This ongoing process of renewal and adaptation ensures that the journey maps stay relevant, providing up-to-date insights that businesses can rely on for making informed decisions.
The enhanced value of journey maps that integrate both behavioural data and Voice of the Customer (VoC) insights is significant, offering a transformative impact on how businesses understand and interact with their customers:
- The accuracy of these integrated journey maps is markedly increased. By combining the objective data of customer behaviours with the subjective feedback from VoC, businesses can create a more precise and true-to-life representation of the customer journey. This approach minimizes the reliance on assumptions or potentially biased feedback, leading to a clearer and more factual understanding of customer experiences.
- Personalization is another critical area where these integrated maps excel. Armed with a deeper and more nuanced understanding of customer behaviours and preferences, businesses can tailor experiences to meet the individual needs of each customer more effectively. This level of personalization is key to creating more engaging and satisfying customer experiences.
- In terms of strategic decision-making, integrated journey maps are a goldmine of actionable insights. They provide a rich source of information that can inform a wide range of strategic decisions, from product development and innovation to targeted marketing strategies and customer service enhancements. This data-driven approach ensures that business strategies are closely aligned with actual customer needs and behaviours.
- The dynamic nature of these integrated journey maps facilitates proactive experience optimization. Unlike static maps, these dynamic versions can be continuously updated and adjusted in response to real-time data, allowing businesses to proactively enhance the customer experience. This agility not only improves customer satisfaction but also fosters stronger customer loyalty, as businesses can quickly adapt to meet and exceed customer expectations.
Comparing approaches side-by-side
This table provides a clear comparison of traditional journey maps, VoC-enhanced maps, and behavioural data-driven maps, highlighting their respective data sources, strengths, limitations, adaptability, predictive power, personalisation capabilities, and cost/resource intensity.
It illustrates how each method fits into the evolving landscape of customer journey mapping, with behavioural data-driven maps emerging as the most comprehensive and dynamic approach.
| Aspect | Traditional Journey Maps | VoC-Enhanced Journey Maps | Behavioural Data-Driven Journey Maps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Source | Assumptions and averaged customer data | Direct customer feedback (surveys, reviews) | Real-time customer behaviour data combined with VoC insights |
| Strengths | Simple to create; foundational understanding; cost-effective | More customer-centric; deeper insights into perceptions; identifies pain points | Comprehensive and accurate; real-time updates; predictive analytics capabilities |
| Limitations | Lacks real-time data and adaptability; based on assumptions; static nature | Subjective; lacks real-time responsiveness; may not represent actual behaviours | Complex and resource-intensive; requires sophisticated data analysis; potential data overload |
| Adaptability | Low; requires manual updates | Moderate; can be updated with new VoC data but not in real-time | High; continuously updated with new behavioural data |
| Predictive Power | Limited; mostly retrospective analysis | Limited; focuses on past and present customer feedback | High; anticipates future trends and customer needs |
| Personalisation | Generalised customer view; limited personalisation | Improved personalisation based on customer feedback | Highly personalised experiences based on actual behaviours |
| Cost and Resource Intensity | Low; minimal reliance on advanced technology | Moderate; requires mechanisms to gather and analyze VoC data | High; needs advanced analytics tools and ongoing data management |
In comparing the three journey mapping methods, traditional maps offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness but lack dynamism and real-time insights.
VoC-enhanced maps bring customer feedback into the equation, providing richer insights into customer perceptions and experiences, yet they still struggle with real-time adaptability and objective behavioural analysis.
Behavioural data-driven maps, however, stand out for their comprehensive and dynamic nature. They integrate real-time behavioural data with VoC insights, offering a highly accurate, adaptable, and predictive view of the customer journey. This evolution underscores a shift towards more nuanced, data-informed strategies in journey mapping, essential for businesses to remain responsive and competitive in a rapidly changing customer landscape.
How to unlock behavioural-based, data-driven journey mapping
The evolution from traditional to behavioural-based, data-driven journey mapping is not just a shift in technique; it’s a fundamental transformation in how businesses understand and engage with their customers.
And, importantly, this transition to more agile, behaviourally informed, and data-driven methods is crucial in an era where customer behaviours and expectations are in constant flux.
Here’s a no-nonsense checklist for how to take the next step in your journey mapping evolution:
Assess your current journey mapping practices
Begin by evaluating your existing customer journey mapping methods. Understand their limitations and identify areas where incorporating VoC and behavioral data could make a significant impact.
Invest in the right tools and technologies
Embrace analytics tools, AI, and data management systems that can integrate and interpret both VoC and behavioural data. The right technology is crucial for making this transition successful.
Train your team
Ensure that your team has the skills and knowledge to leverage these new tools and insights. Consider workshops, training sessions, or partnering with experts in the field.
Start small and scale
Begin by applying these principles to a single customer journey or segment. Learn from this experience and gradually expand to other areas of your business.
Continuously gather and analyse data
Make data collection and analysis an ongoing process. The market and customer behaviors are constantly changing, and your journey maps should evolve accordingly.
Act on your insights
Use the insights gained from your enhanced journey maps to make informed decisions. Whether it’s refining your marketing strategy, improving customer service, or innovating your product line, let your customer insights guide you.
Measure and refine
Continuously measure the impact of the changes you make and be prepared to refine your strategies. Remember, journey mapping is an iterative process.
By adopting a behaviourally informed, data-driven approach to journey mapping, your business can gain a deeper understanding of your customers, anticipate their needs, and deliver experiences that not only meet but exceed their expectations.
Ultimately, this is your opportunity to be at the forefront of customer experience innovation.
Free eBook: The ultimate guide to customer journey mapping