Defining Custom Date Ranges (Studio)
About Defining Custom Date Ranges
You can define and save custom date ranges as filters for your widgets and dashboards.
You can choose static dates or dynamically applied start and end dates. Custom dates work with standard and custom calendars, as long as they include days, weeks, and months.
Types of Custom Date Ranges
When creating a date range filter, you can choose one the following date range types:
EXACT DATE
Exact Date lets you define a fixed time range between two dates. This is a static filter.
FIRST DAY
First Day lets you define a dynamic date range that starts on the first day of the period you select.
This is a daily moving filter, meaning that once a day at 12:00 AM its start and end date will simultaneously shift one day forward.
CURRENT DAY
Current Day lets you define a dynamic date range that uses the current day’s relative place in the time period you select.
A relative place in time is calculated using the following logic:
- Count how many days have passed from the beginning of the current time period until current day.
- Add this number to the beginning of the selected time period.
Current Day is a daily moving filter, meaning that once a day at 12:00 AM, its start and end date will simultaneously shift one day forward.
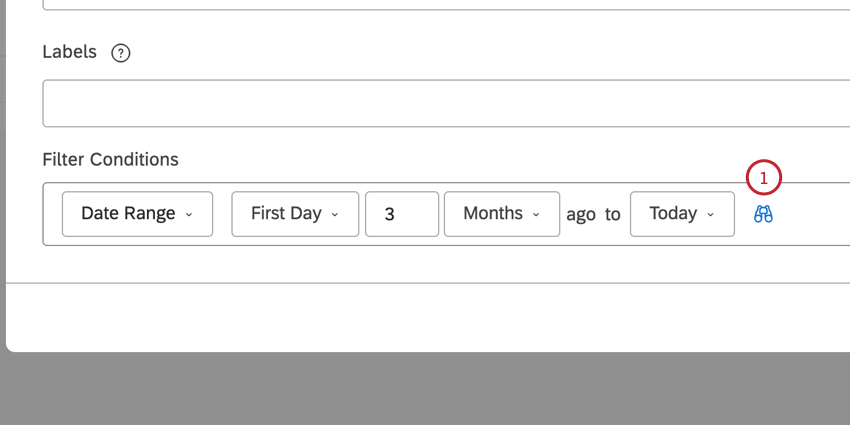
Defining a Custom Date Range
- Open the filter editor by creating a new filter or editing an existing date filter.
- Select Date Range under Filter Conditions.
- Select the type of start date:
- First Day
- Current Day
- Exact Date
Your next steps vary based on what you chose.
First Day & Current Day
Select the number of periods and the time unit to count backwards from.
Then, select an end date. You can choose from the following:
- Today: End a dynamic date range at 11:59 PM on the day this filter is applied.
- Last Day: End a dynamic date range at 11:59 PM on the last day of whatever period you select next.
Example: From the current day 1 quarter ago to the last day 2 months ago.
- Current Day: End a dynamic date range at 11:59 PM using the current day’s relative place in whatever period you select next.
Example: From current day 1 quarter ago to current day 3 quarters ago.
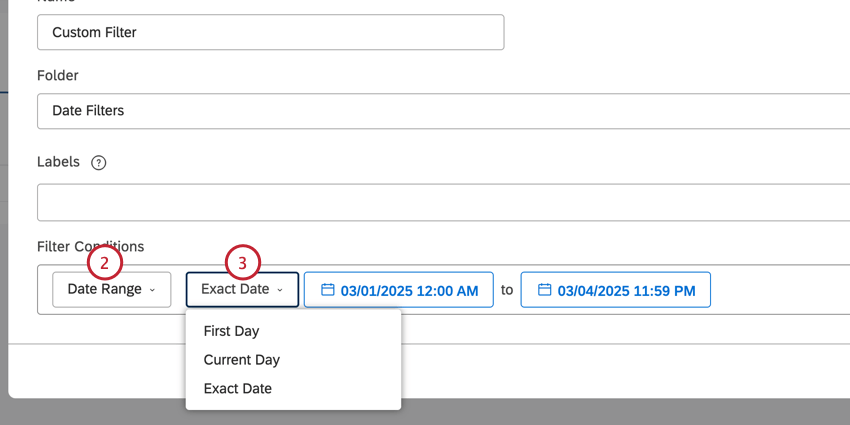
Exact Date
If you chose Exact Date, you will select a start and end date from the calendars. You can quickly navigate months and years from the dropdown, and set the exact time of day.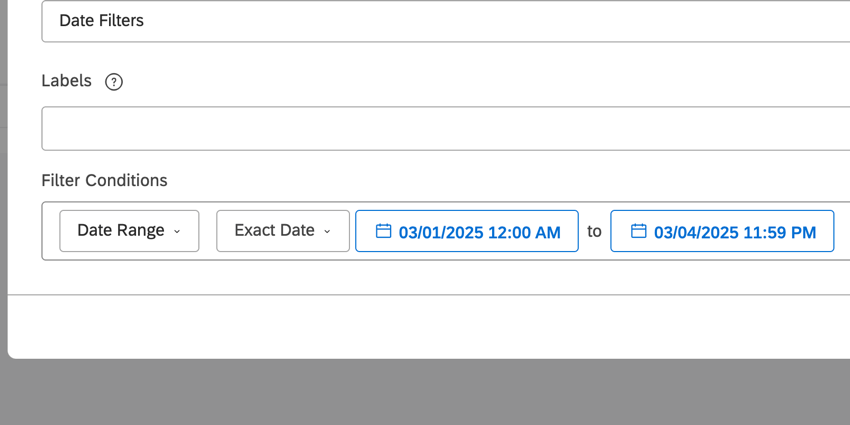
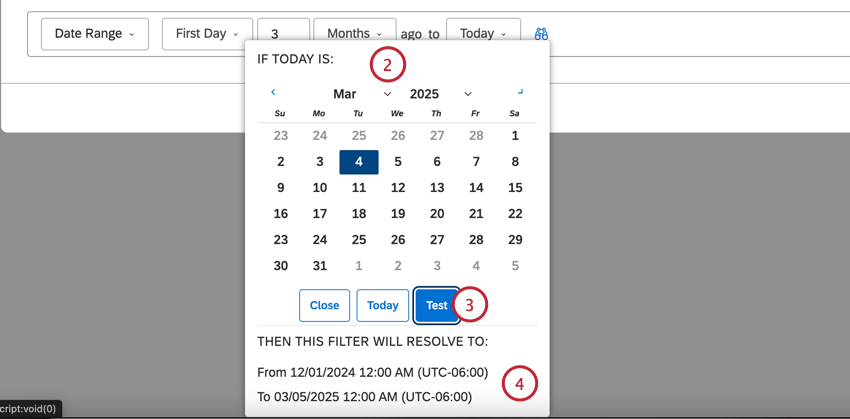
Previewing a Dynamic Date Range
After defining a dynamic date range, you can preview the exact period of data it will show you on any day.
Understanding Automatic Shifts in Zero Time Unit Filters
Consider the following date filter:
You can think of this filter as “all completed months this year.” If you used this filter to look at data on May 16, 2023, you’d see data from January 1, 2023 to April 30, 2023. (You would not see May’s data because May hasn’t completed yet.)
However, let’s say you viewed this filter January 16, 2023. This filter would shift to “all completed months last year.”
There is a special case when a start date defined as “0 [time units] ago” is automatically shifted to “1 [time unit] ago.” (The time unit could be weeks, months, quarters, or years.) The shift occurs when ALL of the following conditions are true:
- The end date is defined by the “last day 1 [time unit] ago” condition.
Example: All completed months, or Last Day 1 Months Ago.
- The end date’s time unit is shorter than the start date’s.
Example: End date defined on months, which are shorter than start date’s year time unit.
- The current date falls within the first end date’s time unit of the start date’s time unit.
Example: All dates in January fall within the first month of the year.
Consider our example from earlier:
Example: First Day 0 Years Ago to Last Day 1 Months Ago.
Depending on the date you view this filter, these are the date ranges you’d see data for:
- If the current date is January 31, 2019, the time period is from January 1, 2018 to December 31, 2018.
- If the current date is February 1, 2019, the time period is from February 1, 2019 to January 31, 2019.
- If the current date is March 1, 2019, the time period is from January 1, 2019 to February 28, 2019.