Filtering by Structured Data (Designer)
About Filtering by Structured Data
Use structured data attributes to filter feedback into models that categorize and display the most relevant information from your dataset. For information on creating and editing filters, see Filtering Data (Designer).
Filtering by Sentiment
XM Discover uses sentiment analysis to determine the overall sentiment of feedback. Sentiment is available as a system attribute with pre-defined bands:
- Negative Sentiment: Feedback with a sentiment score of -5.0 to -1.0
- Neutral Sentiment: Feedback with a sentiment score of -0.99 to 0.99
- Positive Sentiment: Feedback with a sentiment score of 1 to 5.0
Filtering by Language
Use the following discover system attributes to filter by data type:
- CB Auto-detected Language ( _languagedetected ): The language feedback was submitted if your project uses automatic language detection.
- CB Processed Language ( _language ): The language feedback was submitted in. If the language is not supported by XM Discover, it will be marked as “OTHER”.
XM Discover is capable of recognizing and tagging data with over 150 languages using the Automatic Language Detection feature. Without automatic language detection, the following languages are available:
- Arabic
- Bengali
- Chinese (Simplified and Traditional)
- Dutch
- English
- French
- German
- Hindi
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Italian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Romanian
- Russian
- Spanish
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Thai
- Turkish
- Vietnamese
Filtering by Data Type
To filter feedback by the type of data that was submitted, use the following system attributes:
- Source ID ( _id_source ): The data source of the sentences.
- Verbatim Type ( _verbatimtype ): The name of the verbatim field that you would like to filter by. This is useful if you have multiple verbatim columns.
Filtering by Content Type
For projects with content type detection enabled, use the following system attributes to filter feedback from ads, spam, and other non-actionable data:
- CB Content Type ( cb_content_type ): Whether documents are marked as contentful, meaning they contain content, or noncontentful.
- CB Content Subtype ( cb_content_subtype ): Groups documents marked as noncontentful into ads, coupons, article links, or “undefined”.
Filtering by Sentence Type
XM Discover uses semantic analysis to identify intent that’s relevant to your analytics. These categories are used in the sentence-level system attribute: CB Sentence Type ( cb_sentence_type ). Analyzing the type of intent used in your data can help understand how the customer experience can be improved.
Click on the following types of sentences to see what is identified using the sentence type attribute:
- Actionable Sentences
- Suggestions and recommendations on how to improve the customer experience, as well as issues that require immediate attention.
- Churn: Threat of losing clients.
- Cry for help: Requests help and assistance.
- Request: Contains either an implicit or explicit request, such as a call for action or information.
- Suggestion: Contains either an implicit or explicit suggestion to change something.
- Tenure: How long a customer has used a service or product.
- Cancellation: Contains a threat or intention to cancel their membership, service, or other transaction. This type also captures nonrenewal, disenrollment, or termination.
- Sentiment-Related Sentences
- Identifies the sentiment of sentences that lack actionable recommendations.
- Apathetic: Expresses no interest or concern.
- Generic negative: Negative sentiment that lacks a specific target.
- Generic Praise: Positive sentiment that lacks a specific target.
- Recommend: Recommends this customer’s experience.
- Not recommend: Advises against this customer’s experience.
- Question/Answer Sentences
- Types of feedback from answering survey questions.
- Apology: Contains an explicit apology.
- Cross reference: References a previous comment or an answer.
- Don’t know: Feedback is unable to provide an answer. For example, “I wish I knew”.
- Everything: Answers that cover all of the suggested options.
- List: Contains a list of items.
- No comment: Respondent declines to comment or leave an answer. For example, “N/A”.
- Yes: Contains generic affirmations.
- Social Remark Sentences
- Feedback related to the social aspects of the customer interaction, such as greetings, laughter, and gratitude.
- Hello/Bye: Greetings and goodbyes.
- Laughter: Expressions of laughter, either verbally or by use of emojis. For example, “Haha! xD”.
- Thanks: Expressions of gratitude.
- Legal Disclosure Sentences
- Feedback that contains legal disclosures.
- Disclosure: Contains disclosure statements. For example, “This call may be monitored or recorded.”
- Mini-Miranda: Applicable in the United States, contains a Mini-Miranda legal warning. For example, “The purpose of the communication is to collect a debt.”
- Conversation-Specific Sentences
- Feedback specific to contact center conversations. These sentence types are only available with conversational data.
- Empathy: Empathy is expressed, such as apologizing, demonstrating interest, or acknowledging hardship.
- Hold: Clients are placed on hold.
- Transfer: Clients ask to be transferred or representatives transfer a client.
Filtering by Word Count
Use the sentence word count or the document word count attributes to filter your data by the number of words in your sentence or record. The range set in these attributes is inclusive of values. If the word count is zero, the sentence/record either has no text or was loaded before the feature was enabled.
- CB Sentence Word Count ( cb_sentence_word_count ): Sentence-level attribute lets you filter data by the number of words in a sentence.
Qtip: To view sentences with 10 words or less, use the range cb_sentence_word_count: [1 TO 10].
- CB Document Word Count ( cb_document_word_count ): Record-level attribute lets you filter data by the number of words in a record. This is also the sum of all sentence word counts.
Qtip: To view records with 50 words or more, use cb_document_word_count: [50 TO 200].
Filtering by Sentence Quartile
The CB Sentence Quartile ( cb_sentence_quartile ) attribute identifies the part of the verbatim that a sentence follows into. The values are 1-4, with each section representing 25% of the verbatim’s length. If a record has multiple verbatims, there will be quartiles for each verbatim in the record.
Applying Sentence Quartile
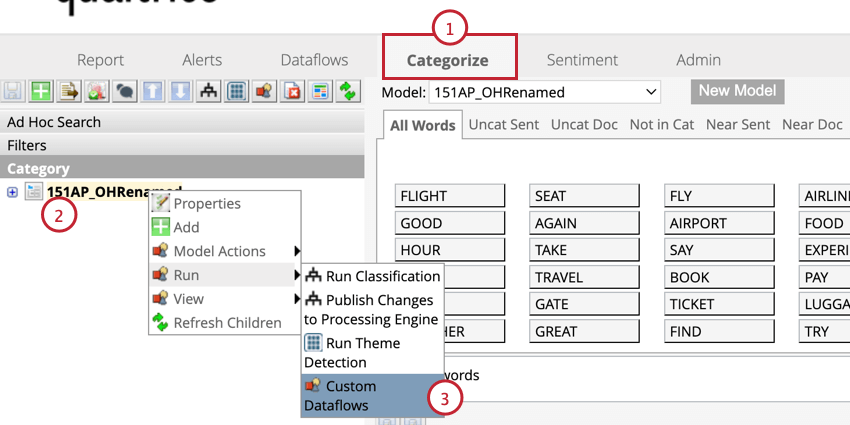
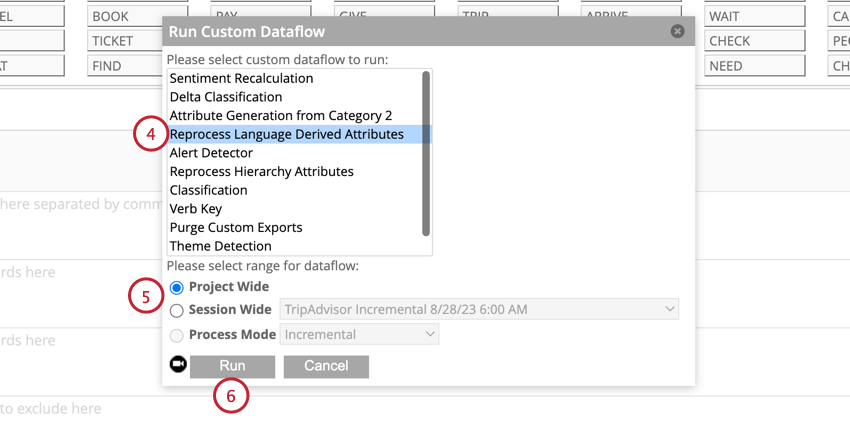
If your historical data is missing sentence quartile data, you can add it to your data.
Filtering by Effort
CB Effort measures the level of effort expressed by customers during their experience. This attribute is available at sentence-level on a scale of -5 to 5, with -5 indicating the hardest experience and 5 indicating the easiest experience. The range is inclusive of values.
Filtering by Loyalty Tenure
CB Loyalty Tenure lets you filter data by the length of time in years that a customer has used a service or owned a product. This attribute is available at sentence-level in sentences with the tenure sentence-type. The range is inclusive of values.
Filtering by Interaction Type
CB Interaction Type ( cb_interaction_type ) defines data by the type of XM interaction, which allows you to distinguish regular feedback from conversational data. This attribute is available at document, verbatim, and sentence levels.
Interaction type can have the following values:
- Chat: Conversational data from digital channels.
- Feedback: Regular feedback data (such as online mention, reviews, and so on).
- Survey: Response data from a survey.
- Voice: Conversational data from transcribed conversations on audio.