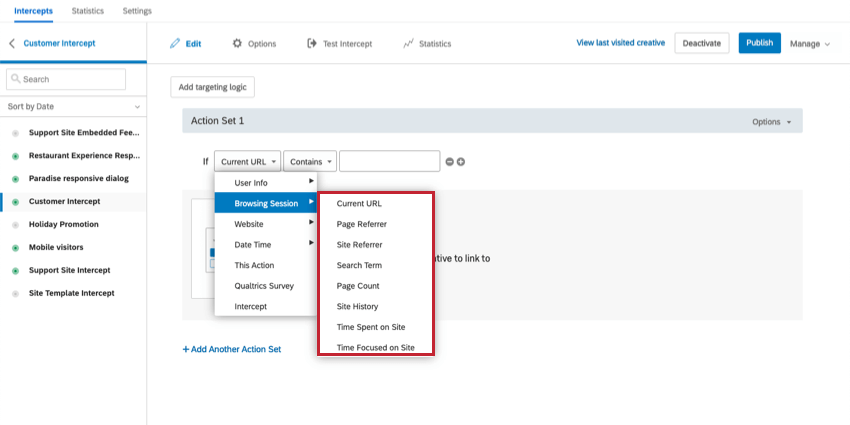
Browsing Session Conditions
About Browsing Session Conditions
Browsing Session conditions allow you to target visitors based on their website behavior. For example, you could provide a feedback survey to visitors who have visited at least three pages of your site, or you could show a coupon to visitors on the shopping cart page.
Current URL
With Current URL, you can target visitors’ browsing activity based on a specific page or set of pages on your website. This is perhaps the most common targeting criteria.
To Create a Current URL Condition
- On either the intercept targeting-level or the action set-level, add logic.
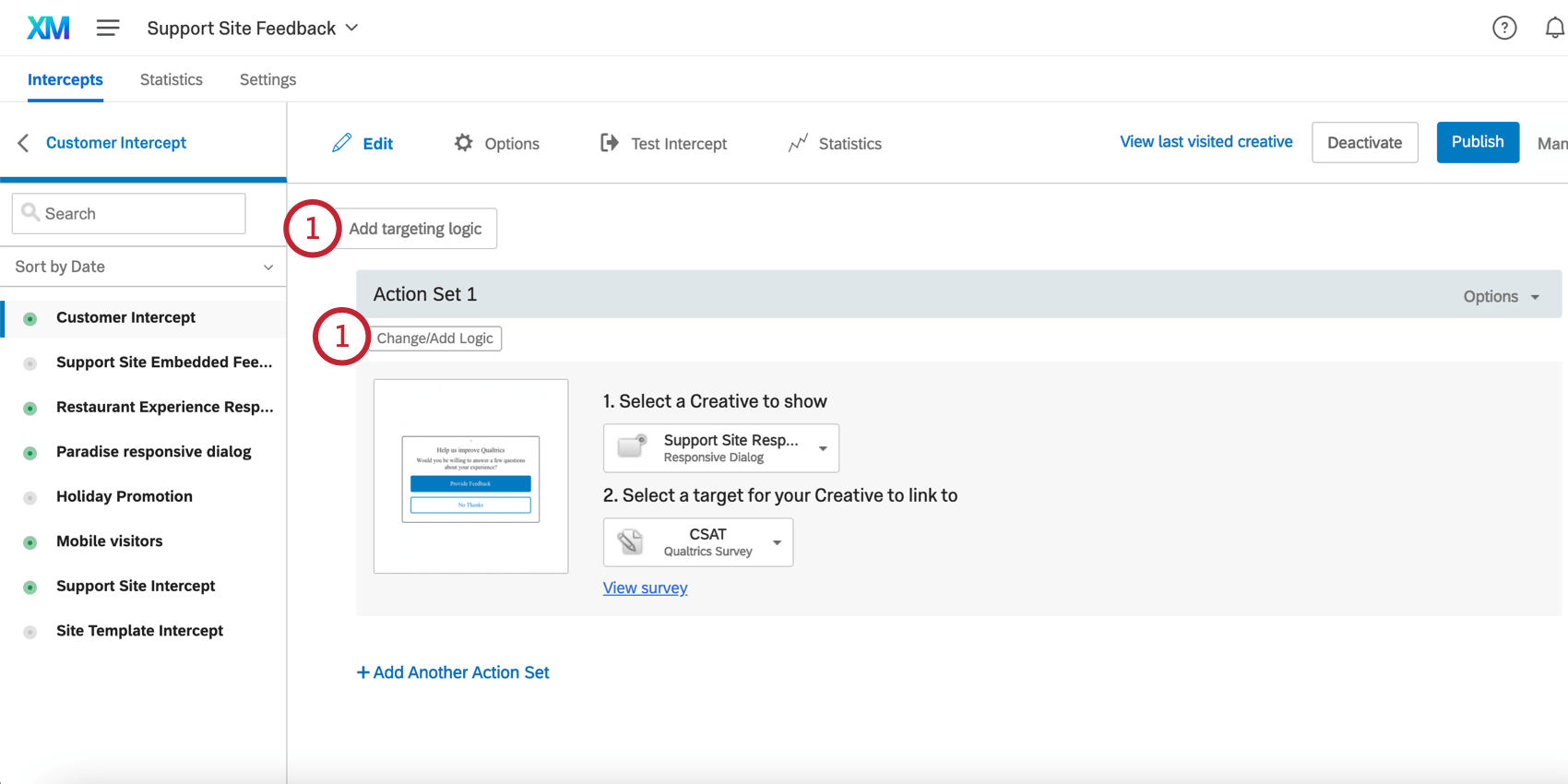
- You’ll notice that Current URL is the default condition. If you are editing an existing condition, select Browsing Conditions, and then select Current URL.
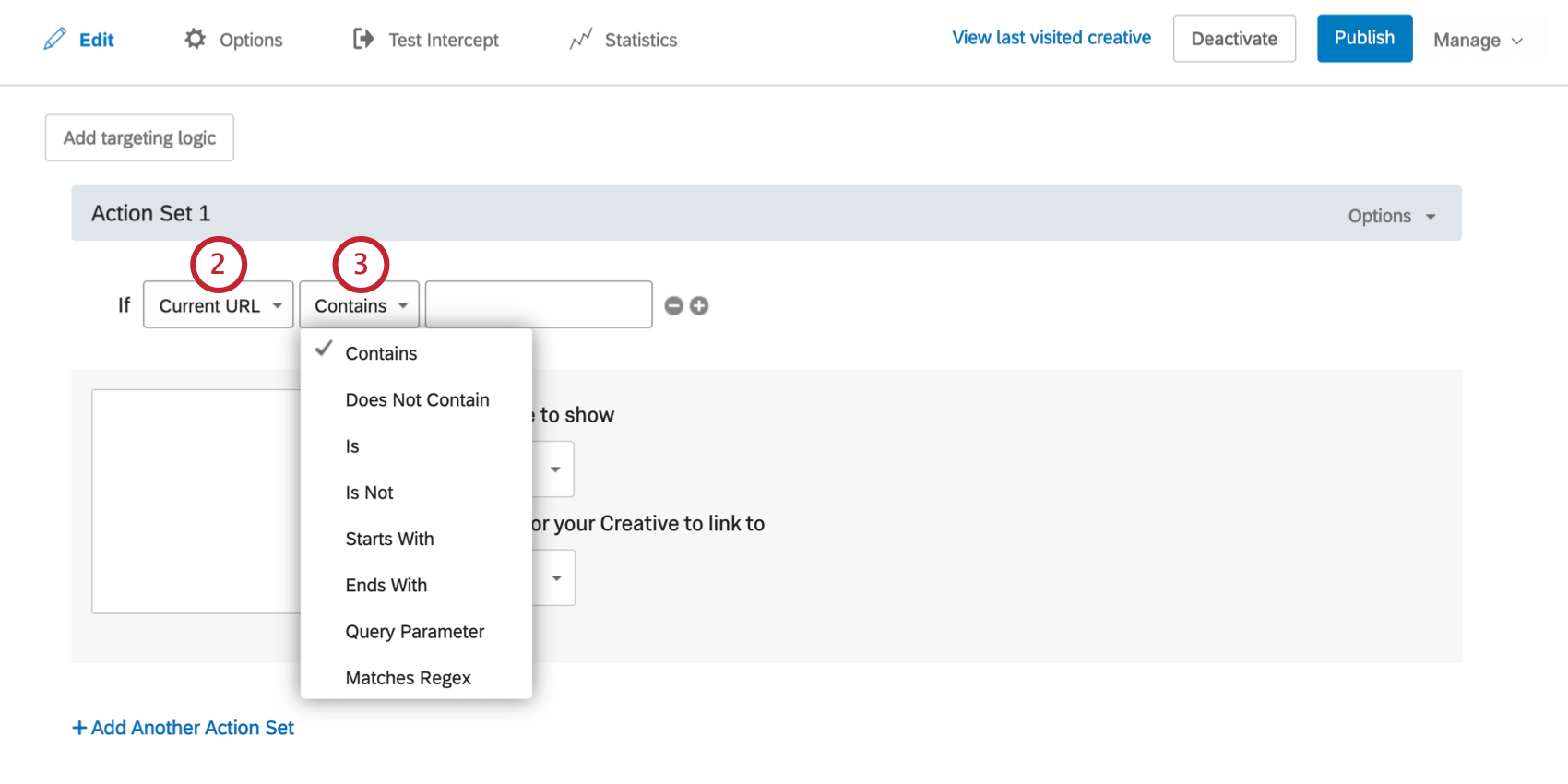
- Choose how you would like to target your value. Here are some commonly used options:
- Is
- Target if the visitor is on a specific page. You will enter an entire URL in the last field.
- Contains
- Target if the visitor is on a page that contains a specific phrase in the URL. For instance, on a clothing website, /new-arrivals/ may be included in the URL of all pages in the new clothing items section.
- Query Parameter
- Target those who have a specific query parameter in the URL. For example if you are A/B testing a page on your website, and have added “&Version=B” to the end of the URL, you could use Query Parameter to check if Version is equal to B.
- Enter the entire URL, a portion of the URL, or a parameter of the URL that you would like to target.
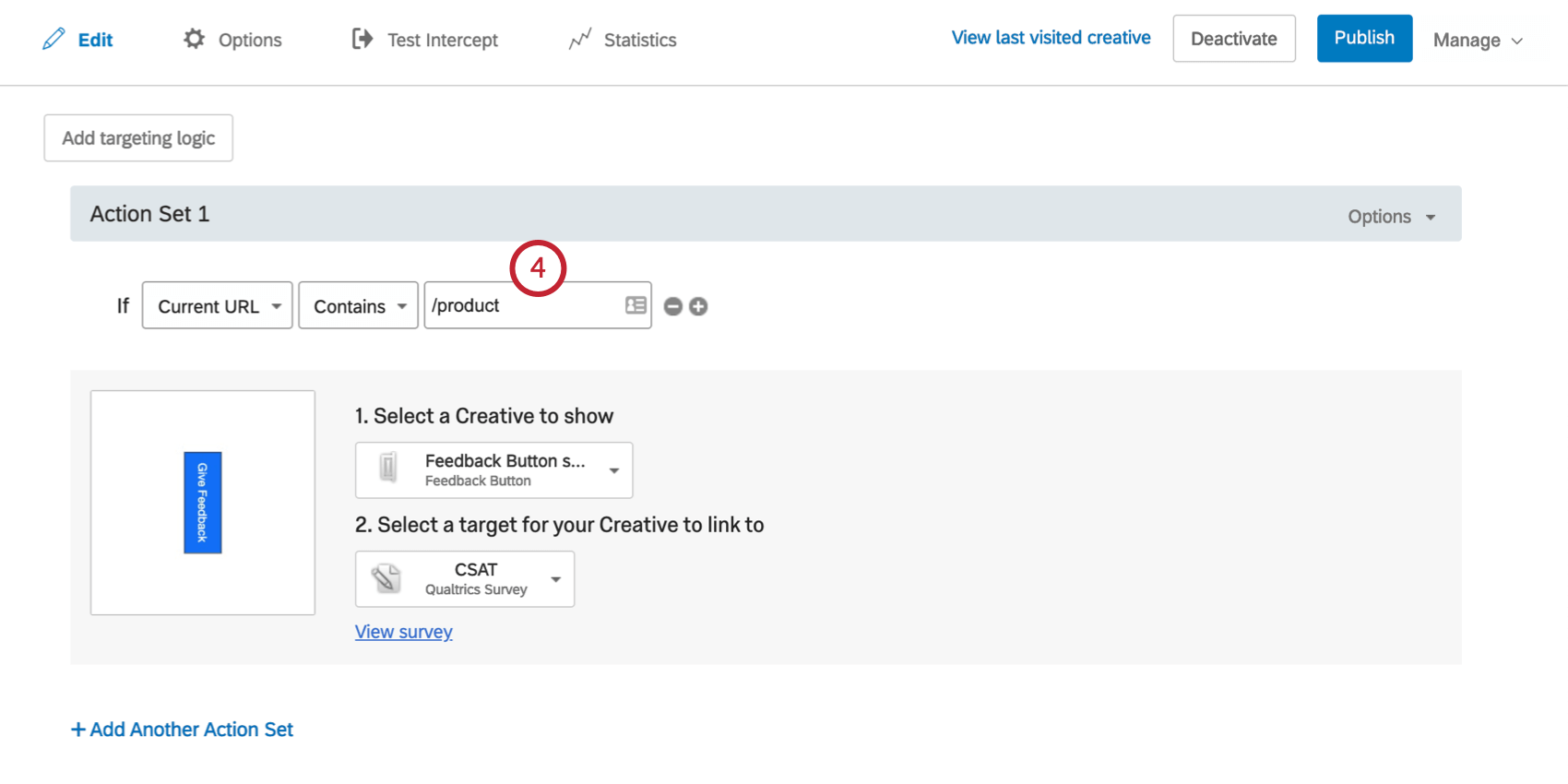
Example: You want an intercept to only display on the homepage of your site, once during the visitor’s session. You could use Current URL logic to specify the visitor must be on your homepage, and combine it with a This Action condition.
As you see above, using Is instead of Contains lets you specify the entire URL in the event that your homepage is your domain URL with no /homepage or other specifiers at the end.
You can also exclude the This Action condition and just turn on Prevent Repeated Display.
Page Referrer
With the Page Referrer condition, you can target visitors based on the page they were on. For example, on a commerce website you might want to offer a coupon to visitors who left the shopping cart page without checking out. To accomplish this, you’d set two conditions: “If Referrer is <shopping cart page>” and “If Current URL is not <checkout page>”.
To Create a Page Referrer Condition
- On either the intercept targeting-level or the action set-level, add logic.

- Drop the first field down.
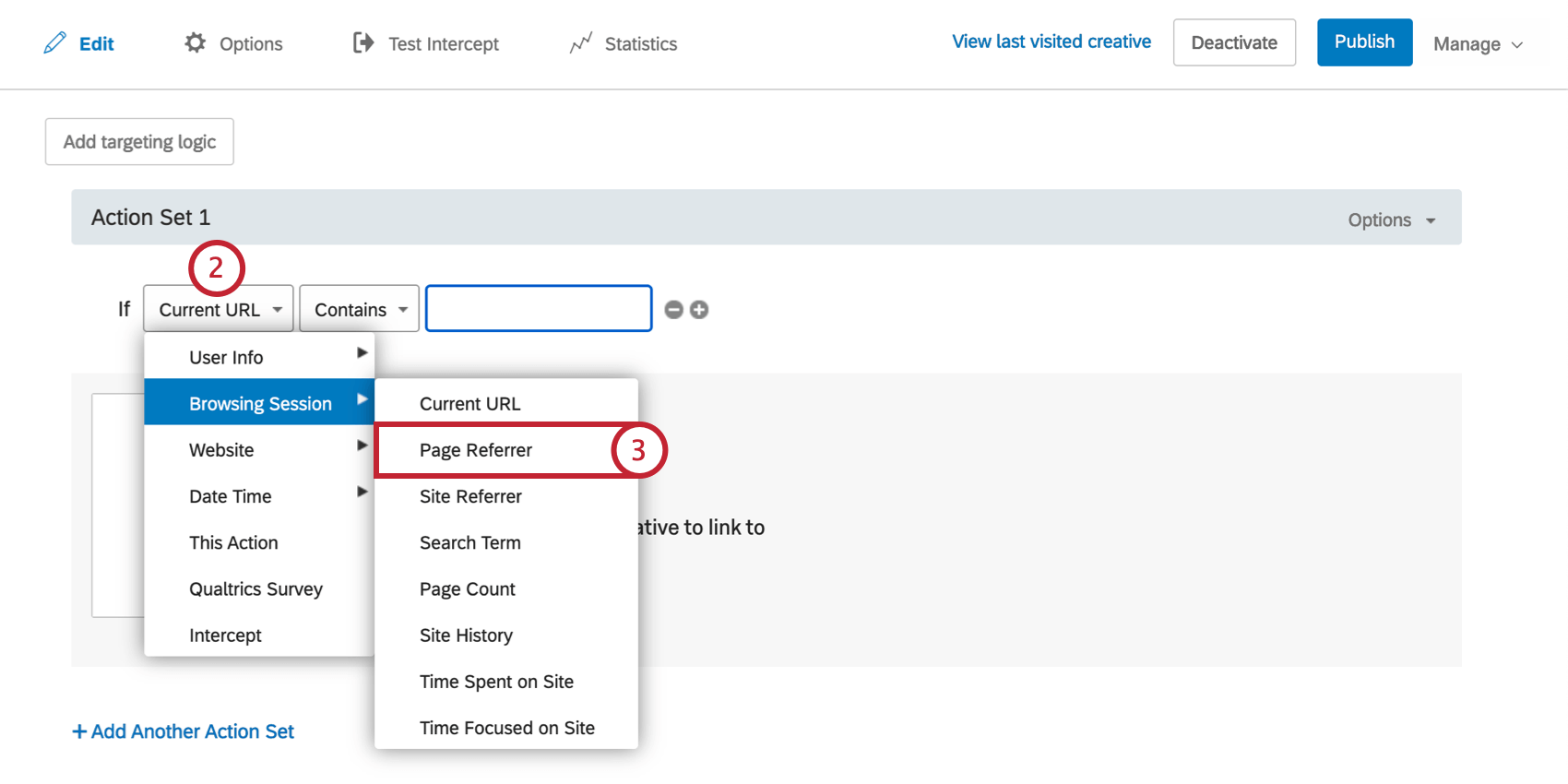
- Select Browsing Session, and then select Page Referrer.
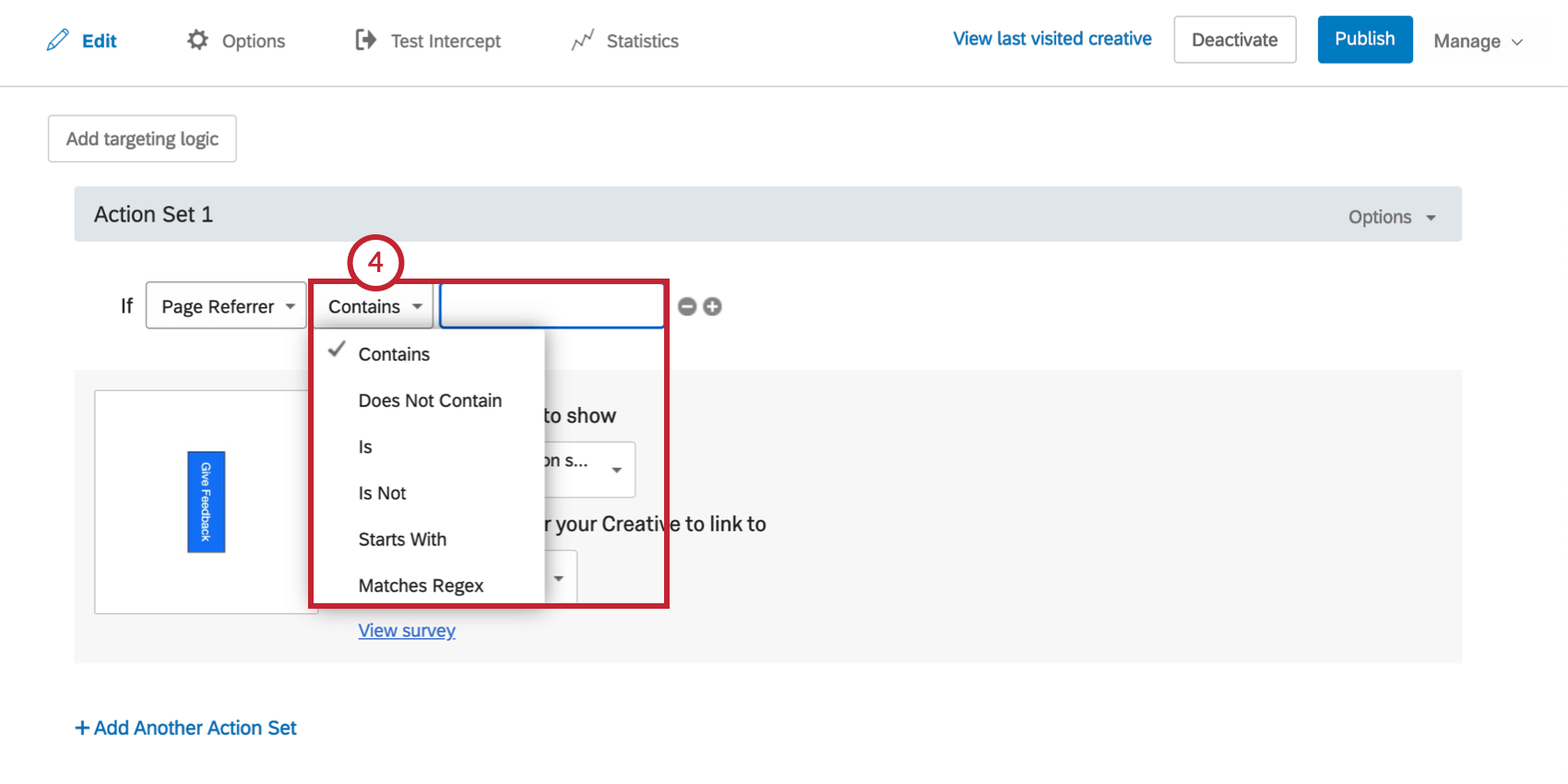
- Complete the logic statement using the same steps described for the Current URL condition.
To test page referrer conditions using the test intercept bookmaklet, you must run the bookmarklet on the referrer page, then navigate to the page with the intercept, and then run the bookmarklet on the page with the intercept.
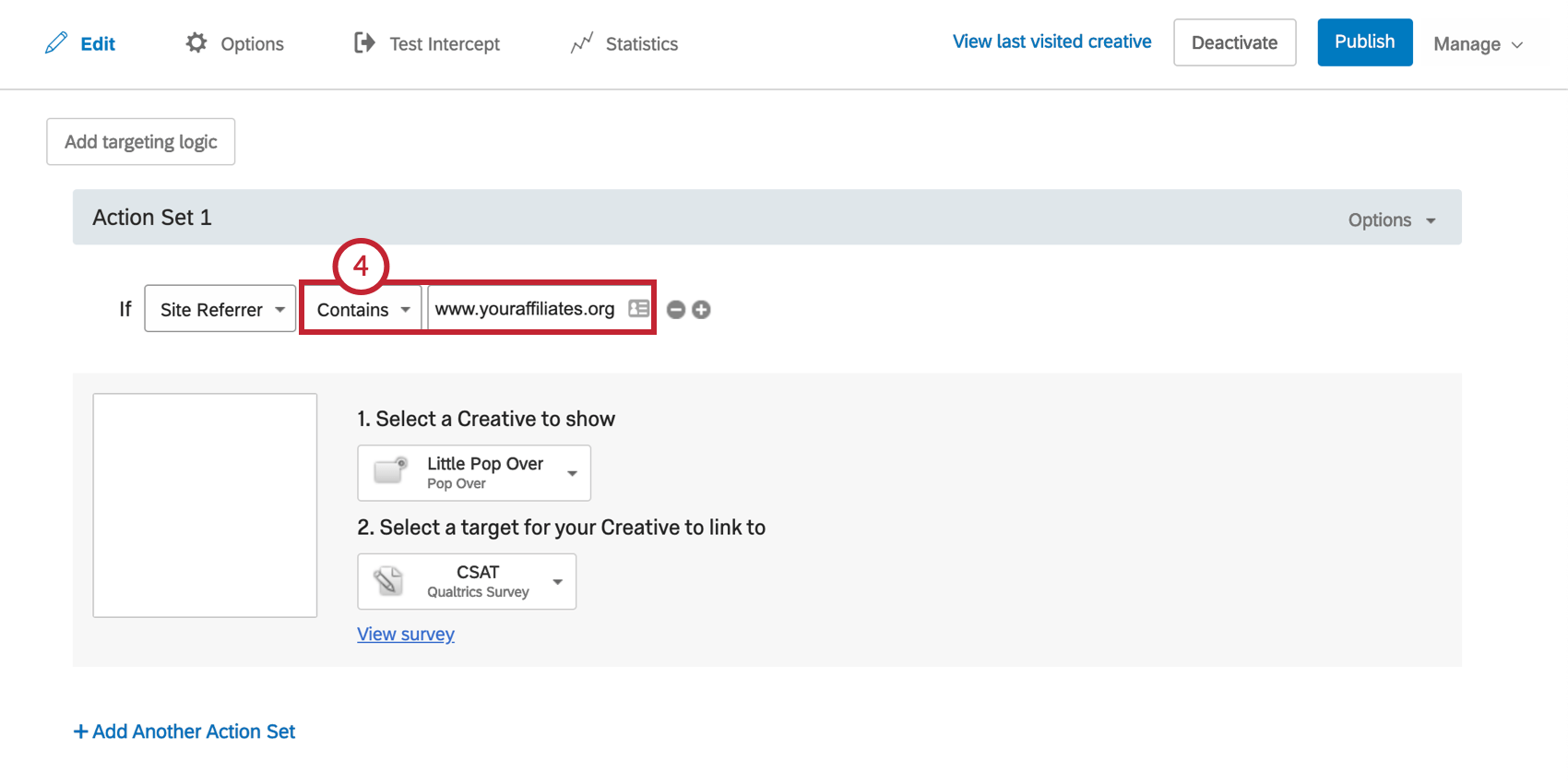
Site Referrer
Use Site Referrer to target visitors based on which website directed them to your website. For example, if a partner website placed a link to your site on their homepage, you could target visitors coming from this link with a special welcome message.
To Create a Site Referrer Condition
- On either the intercept targeting-level or the action set-level, add logic.

- Drop the first field down.
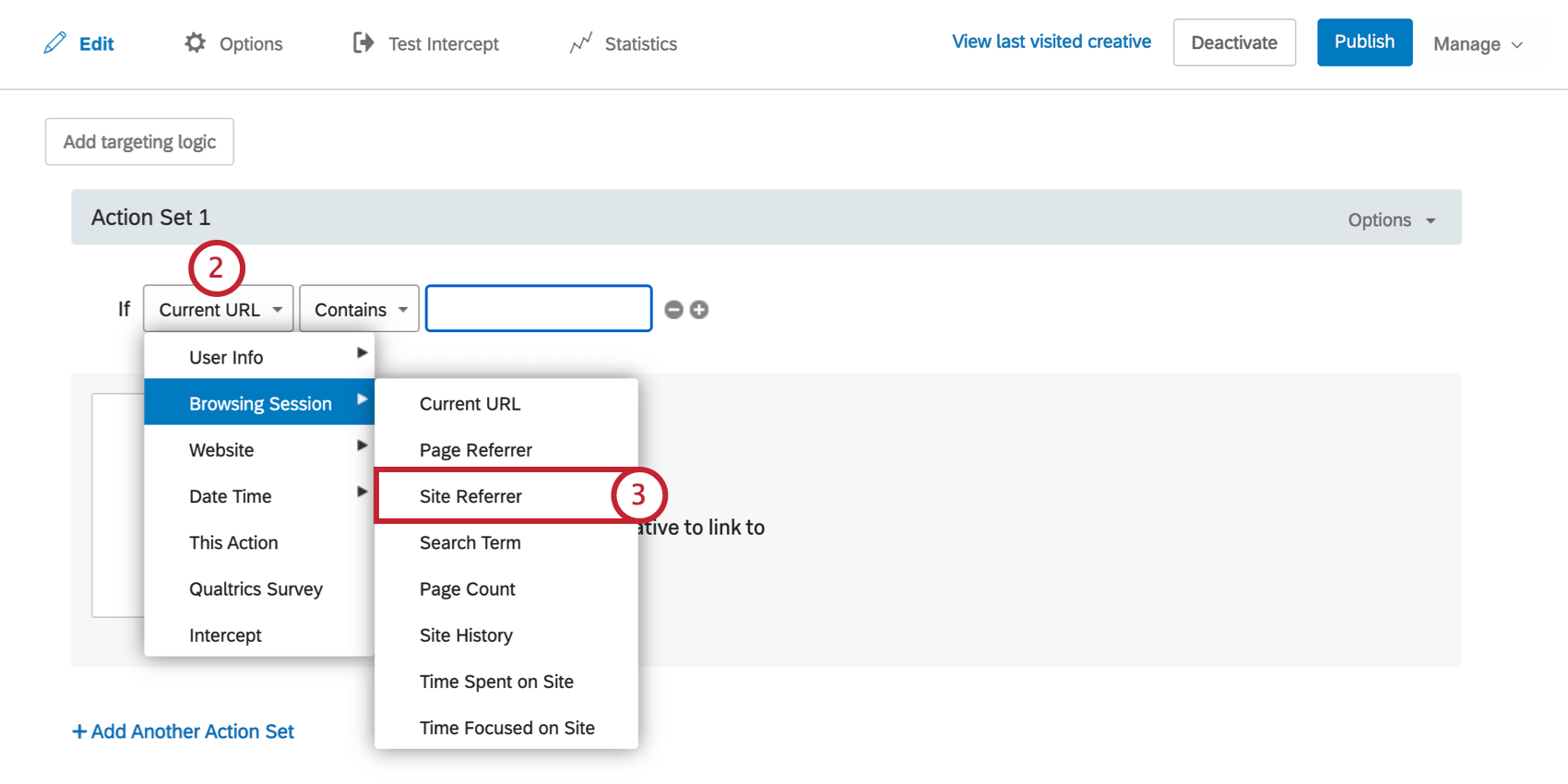
- Select Browsing Session, and then select Site Referrer.
- Complete the logic statement using the same steps described for the Current URL condition.
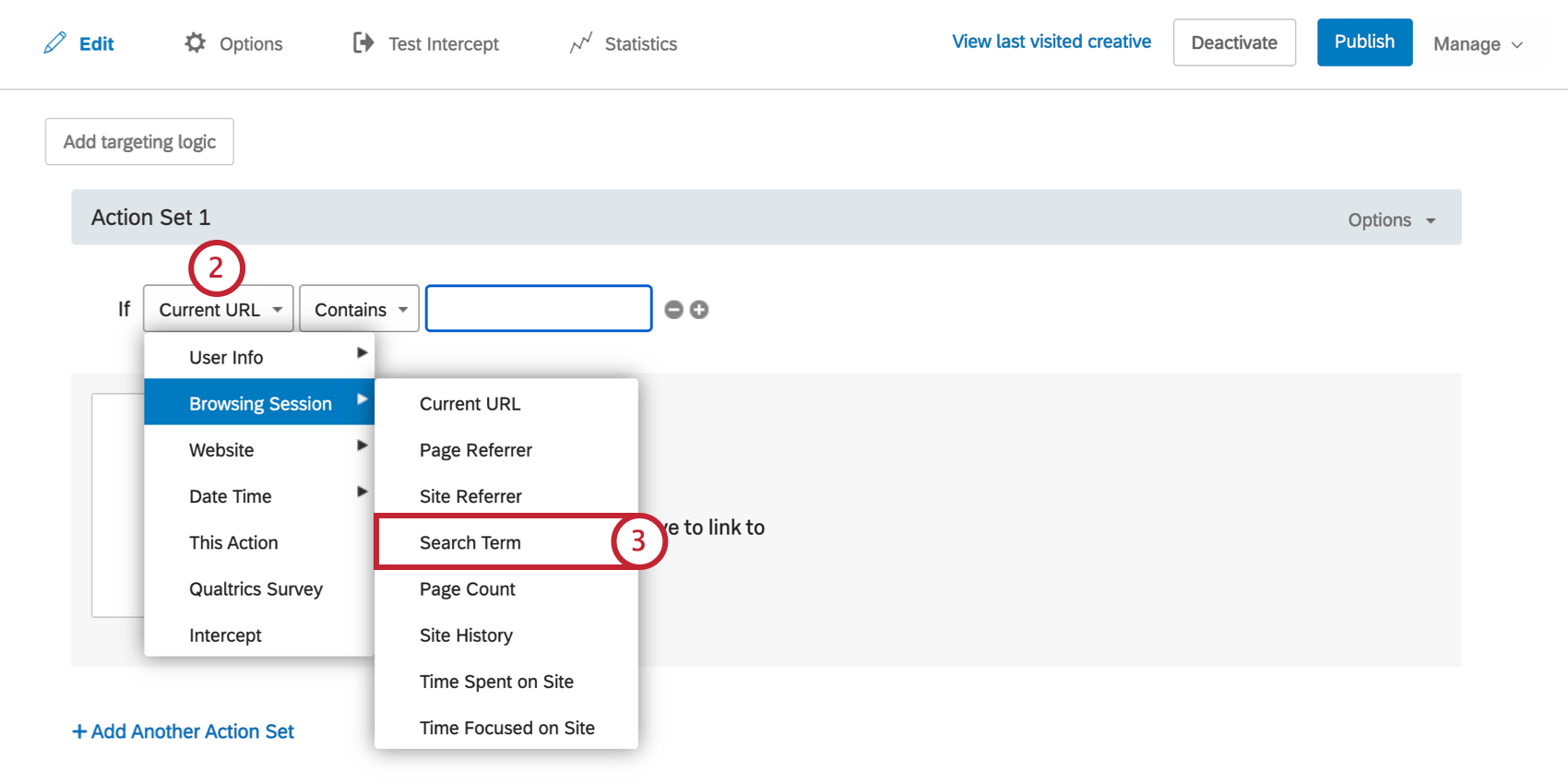
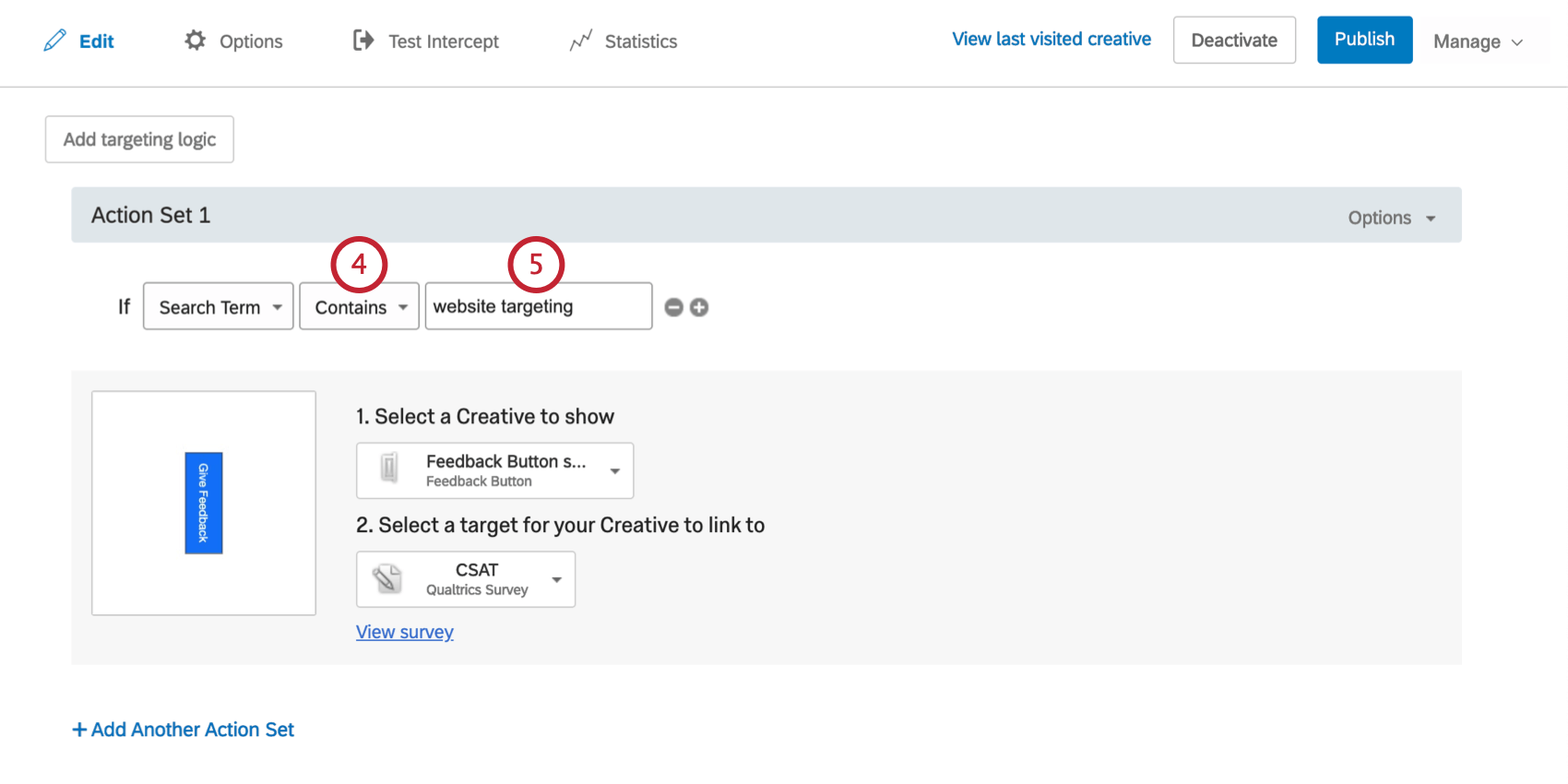
Search Term
Use Search Term to target visitors based on the search term they used to arrive at your website. This works with Google, Yahoo, and Bing search engines.
However, even with this limitation, Search Term can be an effective way to catch visitors.
To Create a Search Term Condition
Page Count
Use Page Count to target visitors based on how many pages they have visited on your website. For example, on a website feedback survey, you may want feedback from visitors who have browsed to at least three pages.
To Create a Page Count Condition
- On either the intercept targeting-level or the action set-level, add logic.

- Drop the first field down.
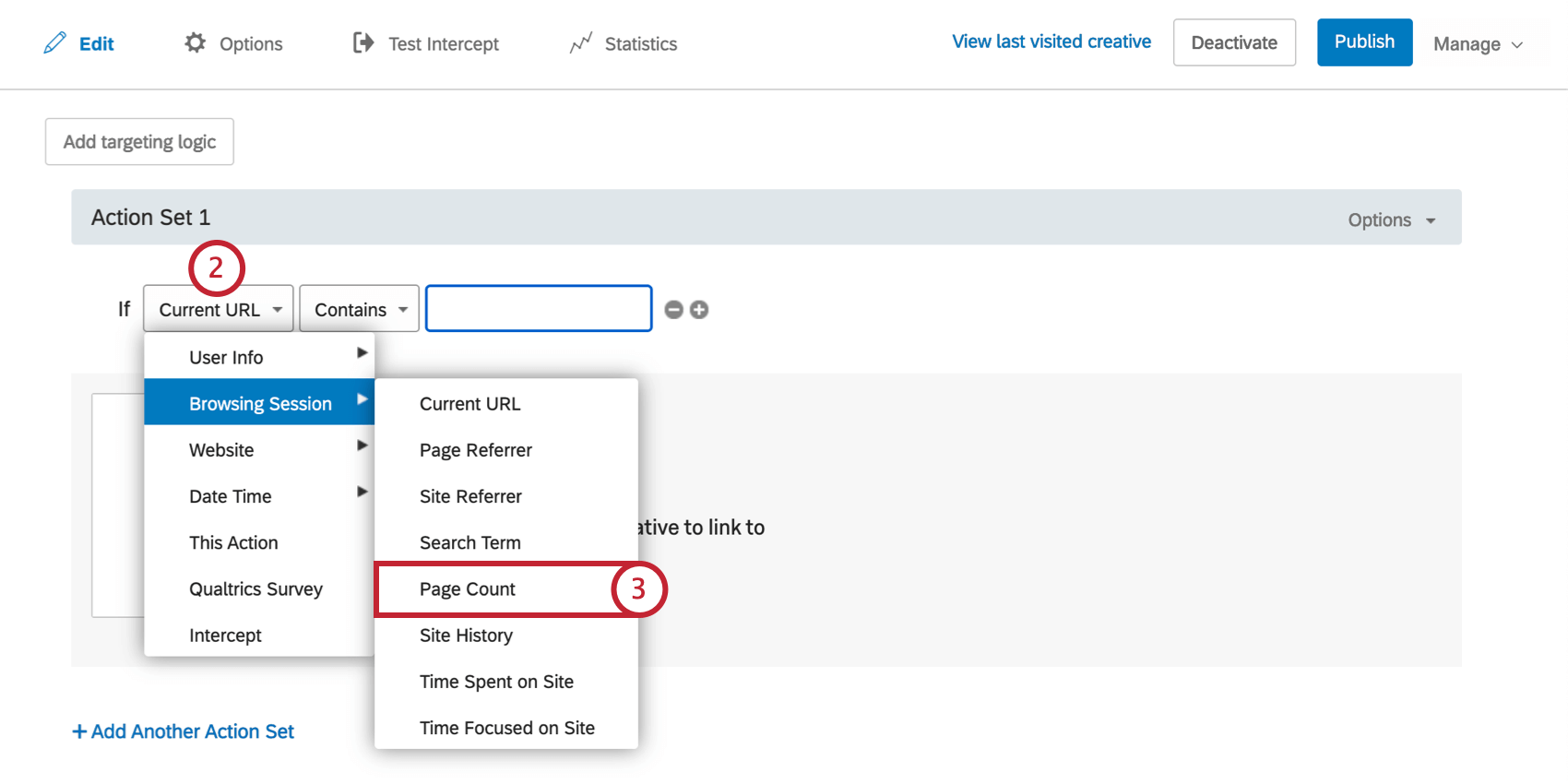
- Select Browsing Session, and then select Page Count.
- Choose whether you would like to target based on Total Pages Visited or Unique Pages Visited.
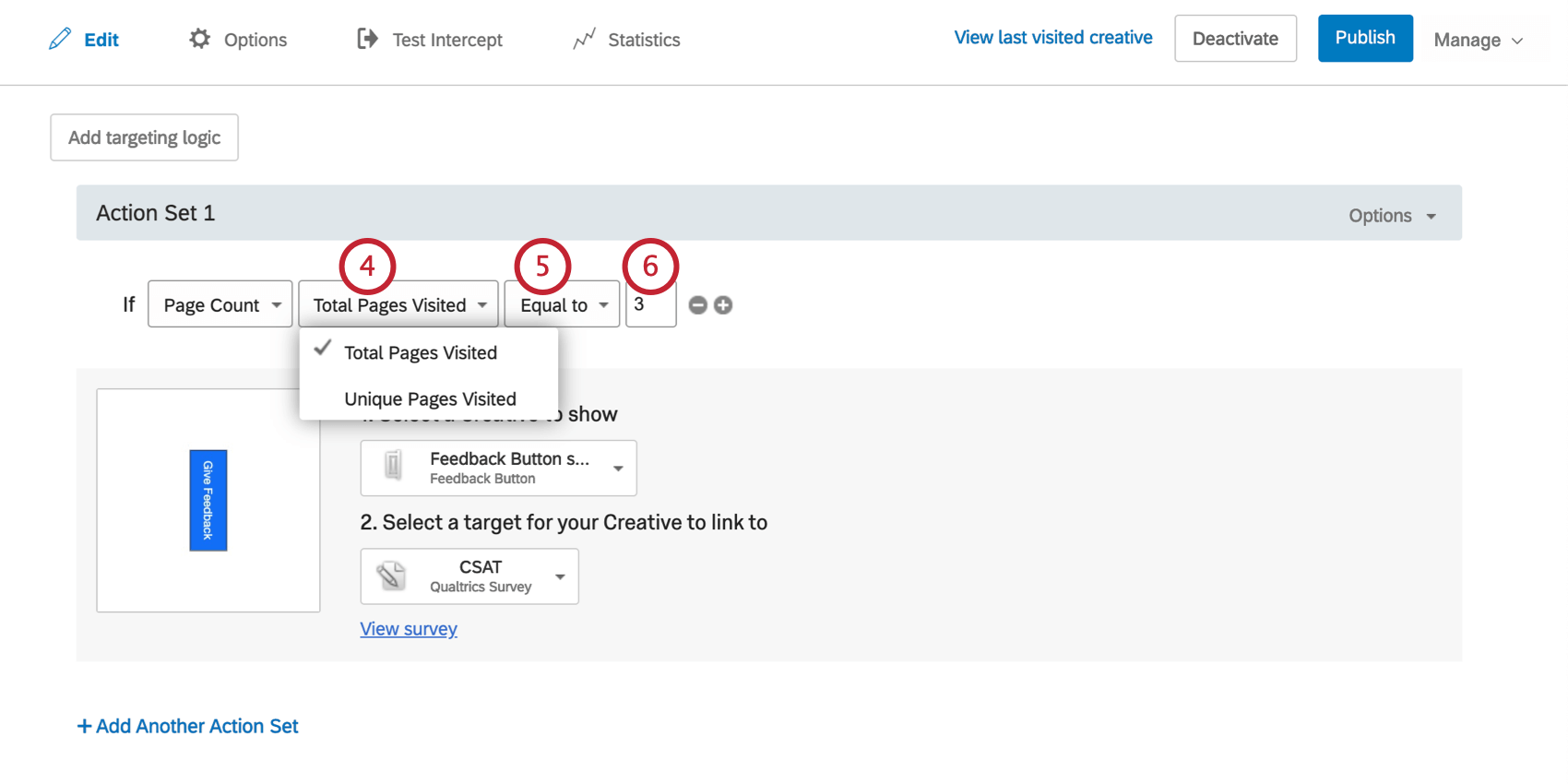
- Indicate whether the pages visited should be Equal to, Not Equal to, Greater Than, Greater Than or Equal to, Less Than, or Less Than or Equal to that number to meet the condition.
- Indicate how many pages you’d like to use for your condition.
Example: You want to display an intercept on any page but the one the visitor entered from. Since this would imply they were on at least 1 page before proceeding through the site, you can add logic that Page Count has to be greater than 1.
For added specificity of what pages the intercept can and cannot be included on, check out Current URL logic above.
Site History
Use Site History to target visitors based on specific pages they have or haven’t been to during their visit. This is often used in conjunction with other conditions. For example, in a site feedback survey, you may want to target those who have been on the website at least 3 minutes and had your homepage as the first page of their visit.
To Create a Site History Condition
- On either the intercept targeting-level or the action set-level, add logic.

- Drop the first field down.
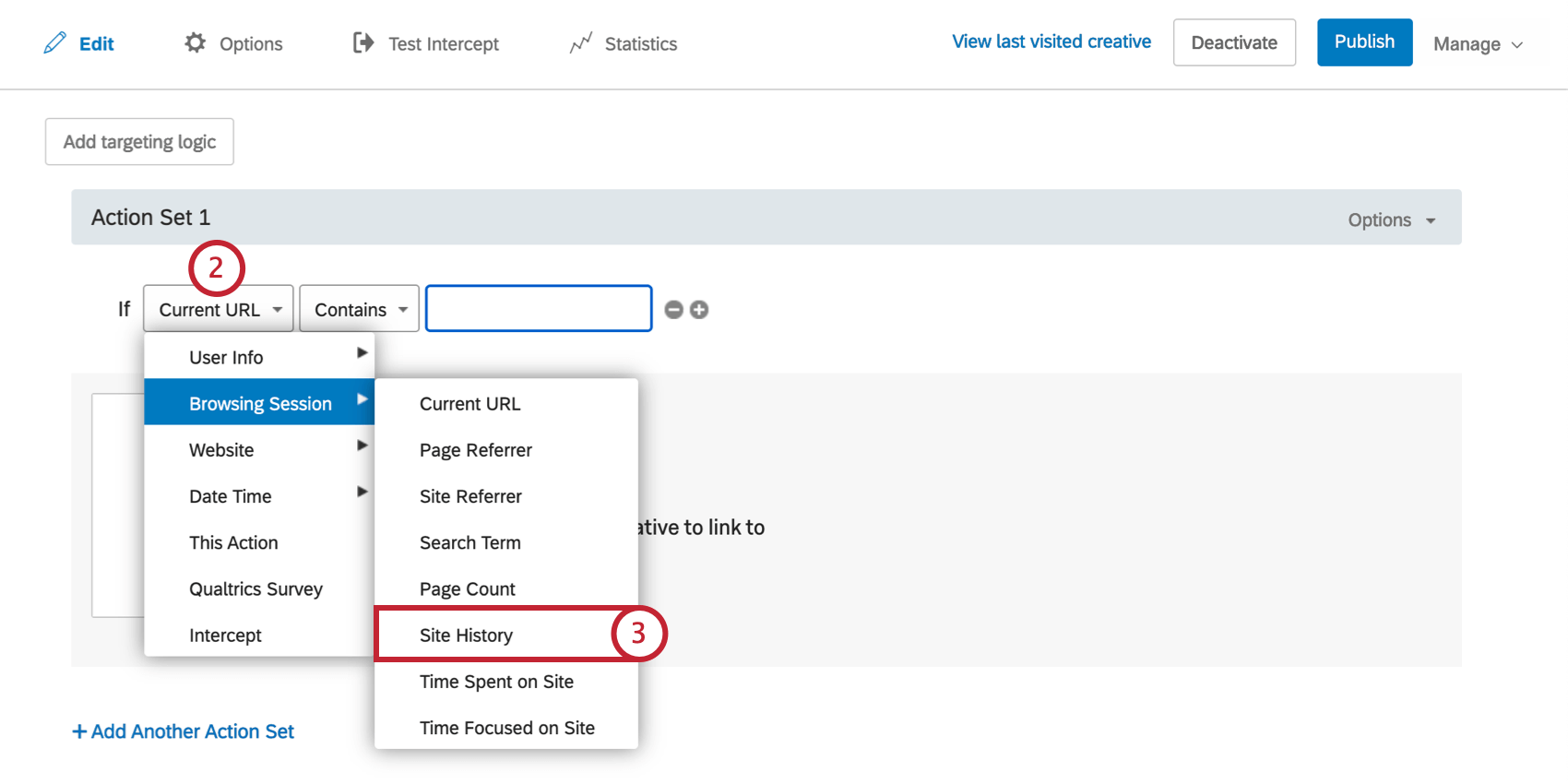
- Select Browsing Session, and then select Site History.
- Select whether you would like to target any Visited URL or Last Visited URL.
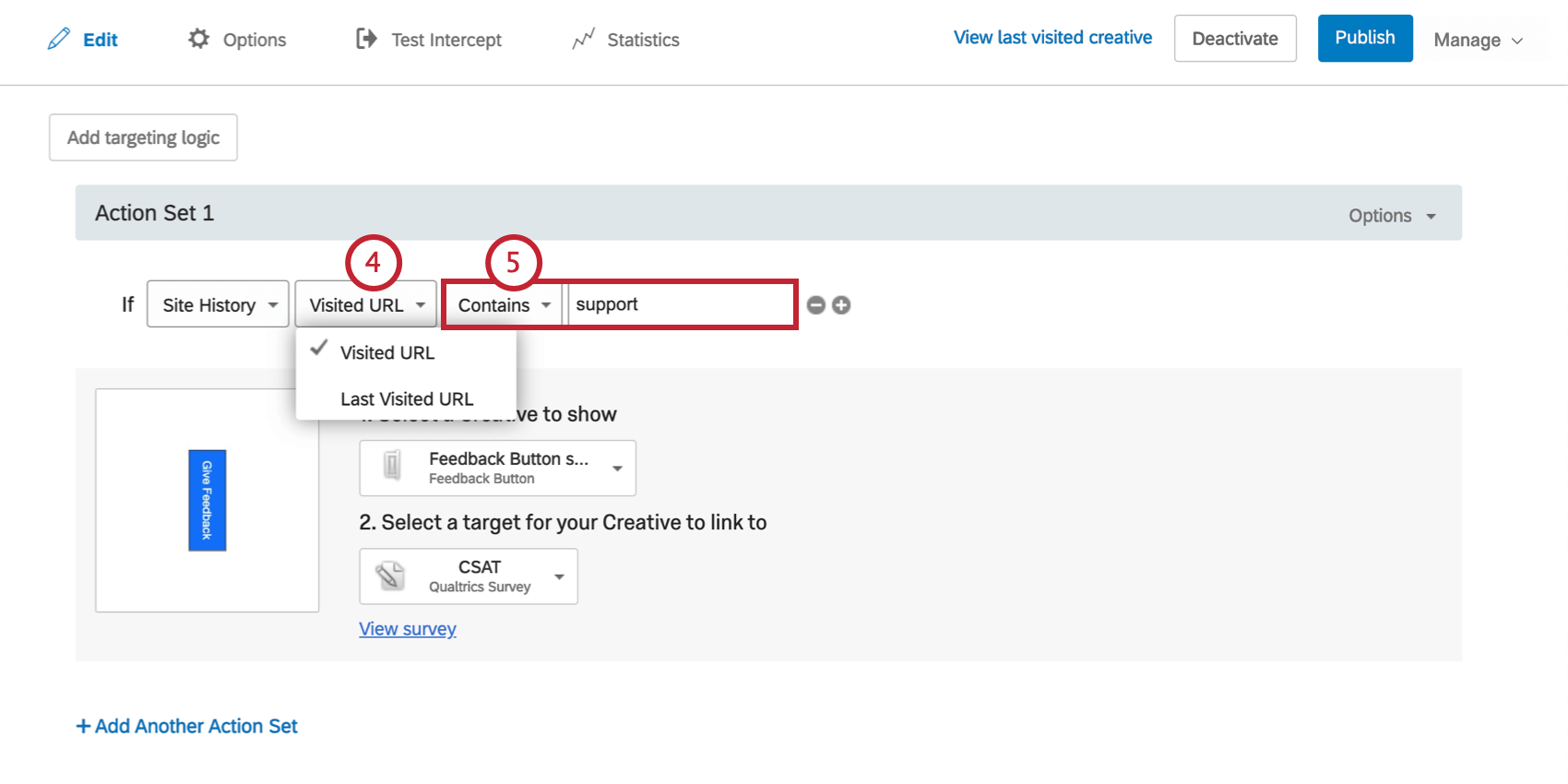
- Complete the logic statement using the same steps described for the Current URL condition.
Time On Site or Time Focused On Site
Use Time Spent On Site or Time Focused On Site to target visitors based on how long they have been on the site.
Time Spent On Site refers to how long the visitor has had your website open in a browser window. Time Focused On Site refers to how long the visitor has had your website open as the front, “in-focus” window on their computer. Time Focused On Site is typically a more accurate indicator of visitor engagement.
To Create a Time On Site Condition
- On either the intercept targeting-level or the action set-level, add logic.

- Drop the first field down.
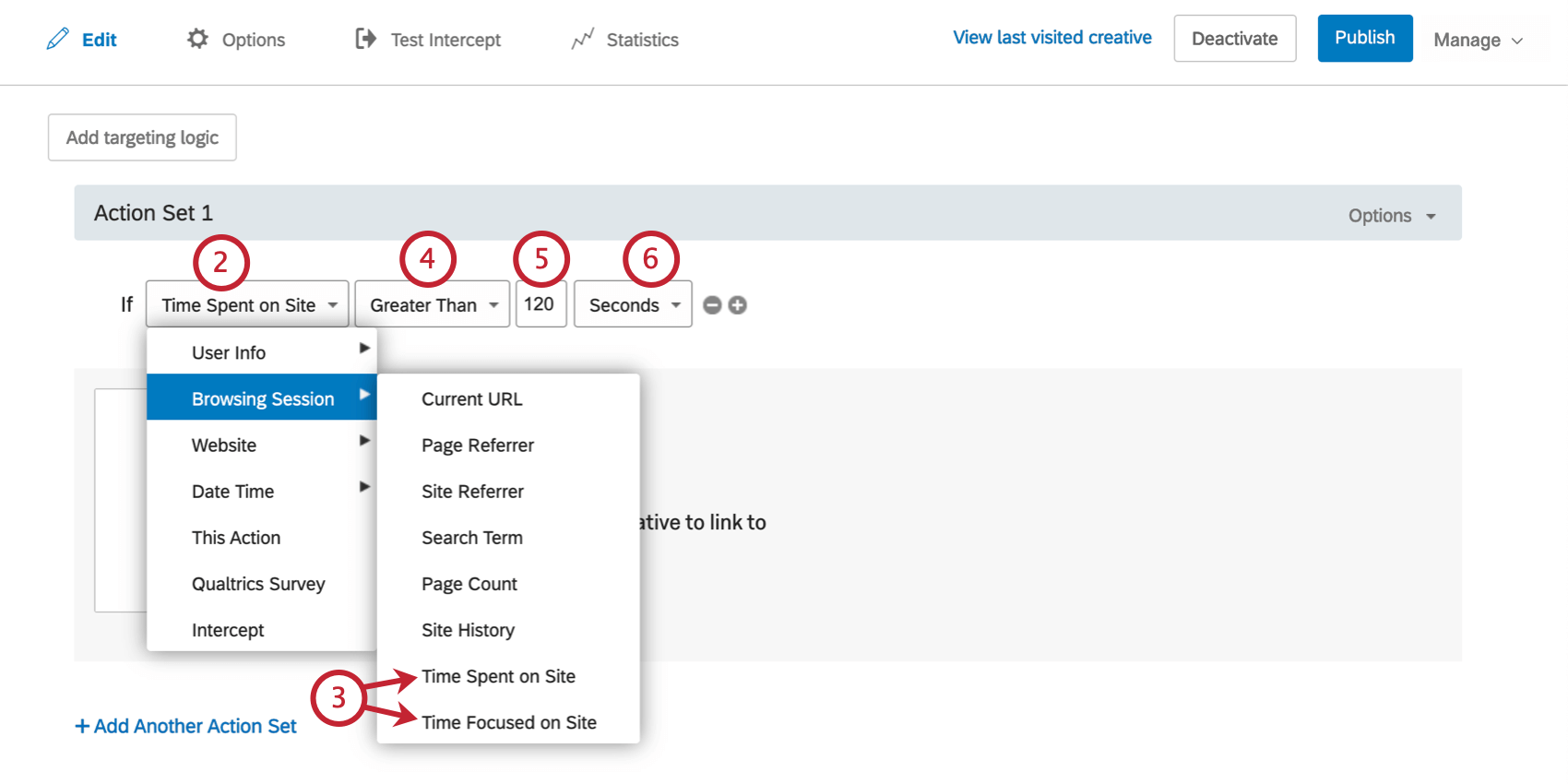
- Select Browsing Session, and then select either Time Spent On Site or Time Focused On Site.
- Select whether you would like to target visitors who have been on the site Greater Than or Less Than the time you will specify.
- Enter the amount of time.
- Select whether that time is in Seconds, Minutes, or Hours.